Abstract
ATP is a known mediator of inflammatory and neuropathic pain. However, the mechanisms by which specific purinergic receptors contribute to chronic pain states are still poorly characterized. Here, we demonstrate that in response to peripheral nerve injury, P2X4 receptors (P2X4R) are expressed de novo by activated microglia in the spinal cord. Using in vitro and in vivo models, we provide direct evidence that P2X4R stimulation leads to the release of BDNF from activated microglia and, most likely phosphorylation of the NR1 subunit of NMDA receptors in dorsal horn neurons of the spinal cord. Consistent with these findings, P2X4-deficient mice lack mechanical hyperalgesia induced by peripheral nerve injury and display impaired BDNF signaling in the spinal cord. Furthermore, ATP stimulation is unable to stimulate BDNF release from P2X4-deficient mice microglia in primary cultures. These results indicate that P2X4R contribute to chronic pain through a central inflammatory pathway. P2X4R might thus represent a potential therapeutic target to limit microglia-mediated inflammatory responses associated with brain injury and neurodegenerative disorders.
Keywords: P2X4, microglia, BDNF, pain, knock-out, mice
Introduction
Among the seven P2X receptors, P2X4 displays the most widespread tissue distribution (Khakh and North, 2006; Burnstock, 2007). In the nervous system, P2X4 receptors (P2X4R) are expressed in neurons of different brain regions (Burnstock, 2007). In CA1 pyramidal neurons P2X4R are expressed postsynaptically (Rubio and Soto, 2001), and are activated during high frequency stimulation and thus participate to synaptic potentiation (Sim et al., 2006). P2X4R are also expressed within the immune system. In inflammatory lymphocytes and monocytes, P2X4R mRNA are the most strongly expressed among all P2X receptors (Wang et al., 2004). Functional and pharmacological approaches have also demonstrated the presence of P2X4 channels in peripheral macrophages, where they are often (but not always) associated with other P2XR, mostly P2X1 and P2X7 (Buell et al., 1996; Sim et al., 2007). Similarly, immunohistochemistry has revealed expression of P2X4R in microglial cells recruited after brain or nerve lesions (Tsuda et al., 2003; Zhang et al., 2006). Because of the lack of a highly specific P2X4R antagonist, deciphering the functional roles of P2X4R in macrophages and microglia still remains difficult. In one study, antisense knock-down of P2X4R expression in spinal microglia provided compelling evidence of their functional involvement in tactile allodynia (Tsuda et al., 2003).
In the healthy CNS, microglia are considered to be in a so-called resting state, although constantly surveying the environment (Biber et al., 2007). On rupture of brain homeostasis, microglia rapidly switch to an activated state, characterized by transcriptional and functional remodelling and by the acquisition of an immuno-competent phenotype (Hanisch and Kettenmann, 2007). Purinergic receptors appear to be key players in microglia signaling, both in their resting and activated states (Färber and Kettenmann, 2006). P2Y receptors regulate motility and cellular chemotaxis, two resting microglia processes (Haynes et al., 2006), whereas in the activated state they mediate phagocytosis (Koizumi et al., 2007). As for P2X receptors, immunohistochemistry data has revealed the expression of P2X4 and P2X7 in microglial cells surrounding brain lesions or regions undergoing neurodegenerescence (Parvathenani et al., 2003), where they are likely to promote a local inflammatory response. Indeed, P2X7 receptor activation leads to the secretion of IL-1ß from microglial cell lines and P2X7-deficient mice do not develop mechanical hypersensitivity associated with neuropathic pain (Ferrari et al., 1997; Chessell et al., 2005). Similarly, P2X4R expressed by activated spinal microglia after peripheral nerve injury promote neuropathic pain (Tsuda et al., 2003).
In vivo, intrathecal injection of ATP-stimulated microglia causes the development of allodynia within a few hours. This has been attributed to the secretion of BDNF by spinal microglia that in turns reduces the tonic inhibition of lamina I GABAergic interneurons (Coull et al., 2005). The subtype of purinergic receptor responsible for this ATP-induced BDNF secretion by microglia is still unknown because microglia express different types of purinergic receptors among which at least two (P2X4 and P2X7) have been shown to promote neuropathic pain. In this study we used P2X4-deficient mice as an animal model to investigate the potential involvement of P2X4R in ATP-mediated BDNF microglial secretion and neuropathic pain.
Materials and Methods
Targeting of the P2X4 gene and generation of mutant mice.
Mice carrying a targeted null mutation of the P2X4 gene have been described previously (Sim et al., 2006). Briefly, a ß-galactosidase-neomycin cassette was inserted in place of the first coding exon of the P2X4 gene. In P2X4 knock-out mice, the P2X4 promoter drives β-galactosidase expression. P2X4+/− mice were fully backcrossed on the C57BL/6 strain (n >20 generations) and then maintained as separate P2X4 knock-out (P2X4−/−) and wild-type (P2X4+/+) lines. Mice were housed under a standard 12 h light/dark cycle with food and water available ad libitum. Mice used in separate tests were age and sex matched to reduce any variation; age varied between 6 and 12 weeks. All procedures fully complied with French legislation (décret 87-848, October 19, 1987, and order, April 19, 1988), which implement the European directive (86/609/EEC) on research involving laboratory animals, and were performed according to the requirements of GlaxoSmithKline and CNRS ethical standards.
Partial nerve ligation.
Cohorts of 15 male P2X4−/− and P2X4+/+ mice were used for this study. On day 0, before surgery, mice were tested as described below to establish baseline thresholds. All mice underwent surgery to partially ligate the sciatic nerve using a method based on that described by (Seltzer et al., 1990). Mice were anesthetized with isoflurane and ∼1 cm of their left sciatic nerve was exposed by blunt dissection at mid-thigh. A suture was then passed through the dorsal third of the nerve and tied tightly. The incision was sutured and the mice were left for 3 d before testing started.
Measurement of mechanical hyperalgesia.
To assess mechanical hyperalgesia, mice were tested for withdrawal thresholds using an analgesimeter on days 3, 7, 10, 14 and 24 post-operation, as previously described (Chessell et al., 2005). Both ipsilateral and contralateral withdrawal thresholds were measured and expressed as ipsilateral/contralateral ratios. Results were analyzed using two-way ANOVA in Statistica (Statsoft Inc.) with genotype and days postsurgery being used as independent variables. Follow-up analysis was performed using Duncan's test and p < 0.05 was considered significant.
Microglia cultures.
Primary microglial cells were isolated from 1 d postnatal mice. Briefly, cortices were homogenized by mechanical dissociation and mixed glial cells were plated for two weeks in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum (Biowest) and 1% penicillin/streptomycin. Cultures were flushed and purified microglial cells were collected before centrifugation and plating. Pure (>95%) microglial cultures were used within 2 d.
Immunocytochemistry and immunohistochemistry.
The following antibodies were purchased from commercial sources: rabbit-anti-BDNF 1/100 (Santa Cruz) and rabbit-anti-BDNF 1/100 (Abcam), mouse anti-β-galactosidase 1/50,000 (Promega), rabbit anti-phospho-NR1 (Ser896) 1/1,000 (Upstate), rabbit anti-Iba1 1/1,000 (Wako). P2X4 antibody (1/500) was produced in the laboratory using the 19 carboxyterminal residues of mouse P2X4 as immunogenic peptide. Tissues were fixed through a transcardiac perfusion of 4% paraformaldehyde in PBS and postfixed overnight. Vibratome sections (50 μm) were permeabilized using 0.1% Triton X-100 in PBS, nonspecific sites were blocked with 10% FCS, 0.1% Triton X-100 in PBS for 30 min at room temperature and incubated overnight at 4°C with primary antibody. After three washes in PBS, sections were incubated for 2 h with secondary species-specific antibody [goat-anti rabbit Alexa488, donkey-anti mouse Alexa594 secondary antibody (Invitrogen)]. Sections were mounted and viewed with a Leica DMRA2 fluorescent microscope. Images were acquired using a cool-snap HQ (PhotoMetrics) digital camera controlled by the Metaview software suite. For immunocytochemistry, cells plated on coverslips were fixed for 10 min with 4% paraformaldehyde in PBS. Immunolabeling and image acquisition were performed as described above.
COS-7 cell transfection.
COS-7 cells (ATCC # CRL-1651) were grown in DMEM supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum and 1% penicillin/streptomycin. One microgram of cDNA encoding mouse P2X4 and/or BDNF-GFP were transfected at a ratio of 1/3 using lipofectAMINE 2000 (Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Western blot.
Microglia and COS-7 cells were homogenized in a lysis buffer containing 100 mm NaCl, 5 mm EDTA, 1% Triton X-100, Complete protease inhibitor mixture (Roche), and 20 mm Hepes, pH 7.4. Lysates were clarified by centrifugation and protein concentration determined using a protein assay kit (Bio-Rad). Proteins were separated on reducing 8% SDS-PAGE, and transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane. The membrane was blocked with 5% nonfat dry milk/0.5% Tween20 in Tris buffer saline (TBST) overnight at 4°C. The membrane was then incubated for 3 h at room temperature with the appropriate antibody diluted in TBST: rabbit anti-P2X4 and anti-P2X7, (1/300, Alomone Laboratories) rabbit anti-GFP (1:2,000, Torrey Pines), rabbit anti-BDNF (1:100, Santa Cruz) and mouse anti-tubulin (1:2,500, Sigma). After three washes in TBST, the membrane was then incubated with species-specific HRP-conjugated secondary antibody for 1 h at room temperature and revealed with ECL+ detection kit (GE Healthcare).
YO-PRO uptake.
Cells were incubated for 10 min with YO-PRO (1 μm, Invitrogen) in a divalent-free solution containing (in mm): NaCl 145, KCl 3, CaCl2 0.1, Hepes 10, pH 7.3 and stimulated with 1 mm ATP in the low divalent solution for 1 min. Fluorescence was excited at 350 nm and emitted light was collected above 540 nm. Images were acquired every 2 s. Analysis of fluorescence was performed with Metaview software. Results are expressed as the mean fluorescence expressed in arbitrary units of all recorded cells (>50) after background subtraction.
Results
P2X4R expression in the spinal cord after PNI was analyzed by immunohistochemistry in WT mice. Ten days after nerve injury, P2X4R expression in the spinal cord was strongly upregulated, ipsilateral to the lesion, whereas in sham animals its presence was barely detectable (Fig. 1A). To investigate the relationship between microglia activation and P2X4R expression, we took advantage of the CX3CR1+/GFP mice, in which eGFP is specifically expressed in microglia within the CNS (Jung et al., 2000). At low magnification, images of the spinal cord showed an increase of the microglial fluorescence ipsilateral to the lesion (10 d post-PNI) compared with control (Fig. 1B). At higher magnification, the typical morphological modifications of activated microglia (thicker and shorter processes, larger cell body) were clearly detected in the dorsal horn, post-PNI compared with sham. In addition, a clear colocalization of eGFP and P2X4R immunostaining further confirmed that after PNI, expression of P2X4R is upregulated in activated microglia (Fig. 1C).
Figure 1.
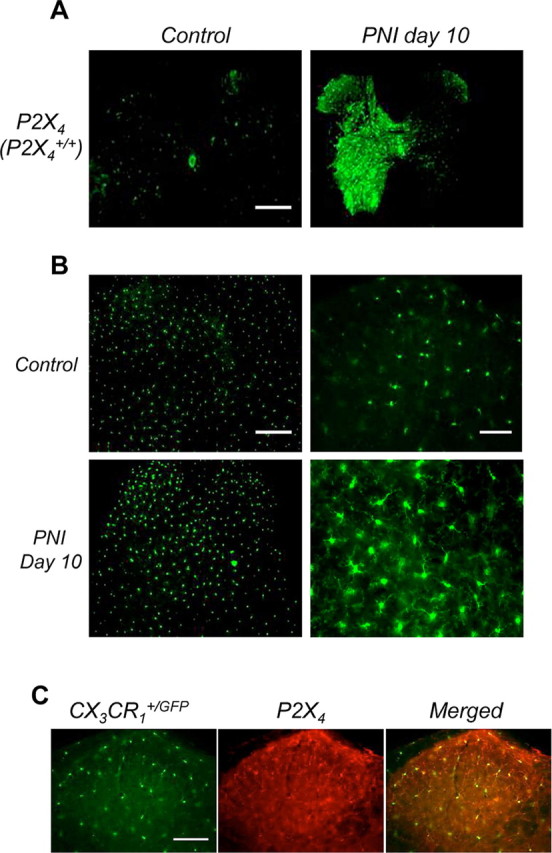
Peripheral nerve injury induces upregulation of P2X4R in activated spinal microglia. A, Comparison of P2X4 expression in the spinal cord in sham-operated and injured mice. P2X4 immunoreactivity was barely detectable in sham animals whereas 10 d PNI, it was clearly induced ipsilateral to the lesion. Note that P2X4 expression spread to the whole side of the spinal cord because of sensory and motor fiber lesions. Scale bar, 500 μm. B, Morphology of spinal microglia in CX3CR1+/GFP mice post-PNI. Compared with sham animals, 10 d post-PNI microglia displayed higher fluorescence intensities, whereas the number of GFP cells was not significantly different. Increase of fluorescence intensity was restricted to the ipsilateral side of the lesion. Scale bar, 500 μm. At higher magnification in the dorsal horn region of the spinal cord (right), post-PNI microglia presented the typical morphological characteristics of the activated state with larger cell bodies and compacted processes compared with microglia from sham animals. Scale bar, 50 μm. C, PNI induces P2X4 expression in activated microglia. In the dorsal horn, P2X4 immunoreactivity colocalized exclusively with microglia-specific eGFP fluorescence in CX3CR1+/GFP mice 10 d post-PNI. Scale bar, 100 μm.
Microglial activation after PNI was analyzed in P2X4−/− mice. We first investigated whether the transcriptional upregulation of the P2X4 gene induced by a nerve lesion was still present in P2X4-deficient mice. Ten days post-PNI a strong increase of β-galactosidase immunostaining was present in the spinal cord, ipsilateral to the lesion. LacZ staining was also observed, particularly in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord (Fig. 2A). As observed for P2X4 immunoreactivity in P2X4+/+ sham-operated mice, the level of β-galactosidase expression in the P2X4−/− sham-operated mice was very low. Microglial activation in P2X4−/− mice was analyzed by immunostaining with Iba1 antibody, a specific marker of microglia. Post-PNI a strong Iba1 staining was found ispilateral to the lesion whereas little staining could be observed on the contralateral side (Fig. 2B). In addition coimmunostaining with ß-galactosidase revealed a strong colocalization of both markers. Microglial P2X7 expression in the P2X4-deficient mice was also monitored in vitro. Both Western blotting and YOPRO uptake experiments demonstrated that P2X7 expression was not different between P2X4+/+ and P2X4−/− mice (Fig. 2C). Together, these results demonstrate that P2X4 gene deletion does not affect microglial activation in vivo and in vitro.
Figure 2.
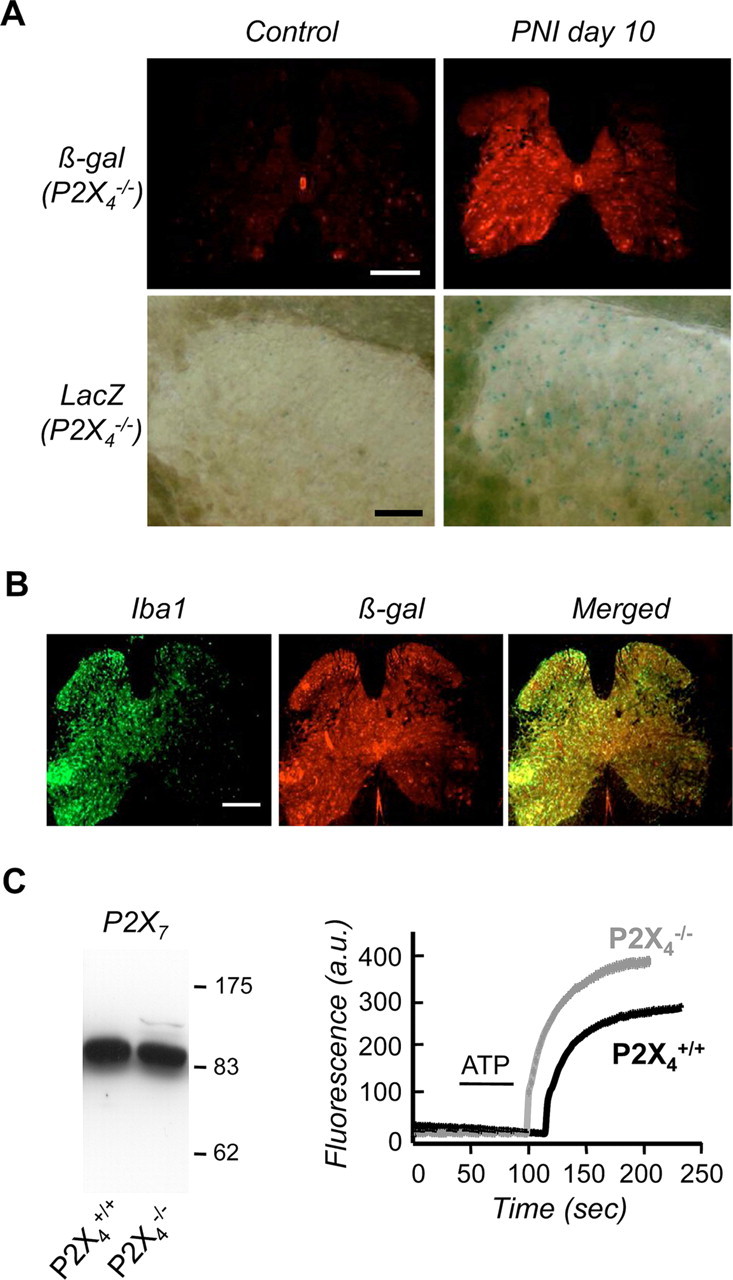
Microglial upregulation of P2X4 gene expression induced by PNI is still present in P2X4-deficient mice. A, In P2X4−/− mice, PNI induced β-galactosidase expression in the spinal cord ipsilateral to the lesion whereas no expression was detected in sham animals. Top row, β-Galactosidase immunoreactivity in spinal cord; bottom row: LacZ staining in the dorsal horn (scale bar, 500 μm). B, Post-PNI, ß-galactosidase immunoreactivity (red) colocalized with the microglial marker Iba1 (green). Scale bar, 500 μm. C, P2X4-gene deletion did not affect P2X7 expression and function in microglia. Western blot of P2X7 expression (left) and ATP (1 mm) induced YOPRO uptake in primary microglial culture from wild-type and P2X4−/− mice (right). Representative experiment of 3 showing mean fluorescence intensity of all recorded cells (>50) after background substraction.
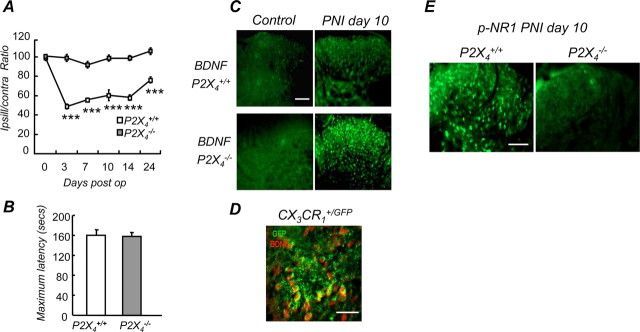
Mechanical hypersensitivity induced by PNI was measured using a Randall-Selitto test in both P2X4+/+ and P2X4−/− mice. P2X4+/+ mice developed strong mechanical hyperalgesia throughout the testing period (days 3–24) (p < 0.005), whereas in the P2X4−/− mice no significant difference was observed compared with baseline (Fig. 3A). Analysis of rotarod data did not reveal any significant difference in latencies between P2X4−/− and wild-type mice (Fig. 3B), ruling out a possible implication of P2X4R expressed by spinal motor neurons in the observed phenotype.
Figure 3.
Lack of mechanical hypersensitivity and altered BDNF signaling in P2X4-deficient mice after peripheral nerve injury. A, Time course of mechanical hypersensitivity induced by sciatic nerve ligature in wild-type and P2X4−/− mice expressed as ipsilateral/contralateral ratios. No hypersensitivity was observed in the P2X4−/− mice, whereas wild-type mice develop a strong hypersensitivity lasting >23 d, (n = 15 mice, two-way ANOVA, ***p < 0.005). B, Sensorimotor coordination was measured using the rotarod test. No difference between wild-type and P2X4−/− mice was observed, ruling out a potential motor deficit in the P2X4−/− mice. C, BDNF immunoreactivity in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord was analyzed by immunohistochemistry in wild-type and P2X4−/− mice. In sham-operated mice, BDNF immunoreactivity was not detected in either wild-type or P2X4−/− animals (left). Ten days post-PNI (PNI day 10), BDNF immunoreactivity was slightly increased in wild-type mice, whereas a strong immunoreactivity was observed in the P2X4−/− mice. Scale bar, 100 μm. D, In the dorsal horn of CX3CR1+/GFP mice 10 d post-PNI, BDNF immunoreactivity (red) colocalized with microglial eGFP fluorescence (green). Scale bar, 50 μm. E, PNI-induced phosphorylation of the NR1 subunit in dorsal horn neurons was impaired in P2X4−/− mice. Levels of phosphorylation of NR1 were analyzed by immunohistochemistry. Scale bar, 100 μm.
ATP-mediated BDNF release from microglia has been linked to the development of allodynia associated with nerve injury (Coull et al., 2005). We investigated whether BDNF signaling in the spinal cord was altered in P2X4−/− mice after peripheral nerve lesion. Ten days postinjury, BDNF immunostaining in the dorsal horn was strongly enhanced in P2X4−/− compared with wild-type mice; no difference between genotypes was observed in sham-operated animals (Fig. 3C). After PNI, BDNF immunostaining colocalized with the microglial marker GFP in the CX3CR1+/GFP mice (Fig. 3D). BDNF is known to induce phosphorylation of the NR1 subunit of the NMDA receptors expressed in dorsal horn neurons (Slack et al., 2004). Ten days post-PNI, immunofluorescence of p-NR1 was strongly reduced in P2X4−/− mice when compared with wild-type animals (Fig. 3E). Altogether these results suggest that BDNF released from microglia is impaired in P2X4−/− mice.
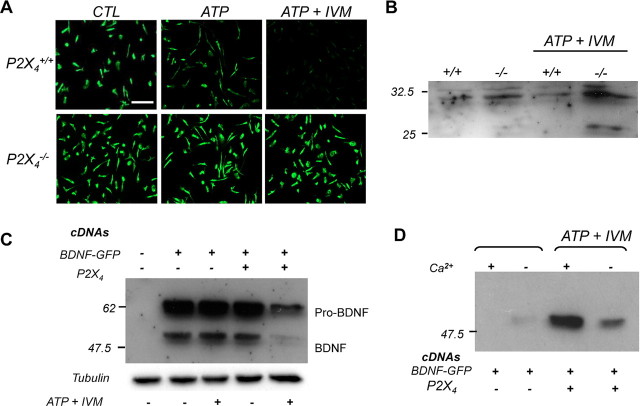
ATP-induced secretion of BDNF by microglia was further investigated in microglia primary cultures from wild-type and P2X4−/− mice. Intracellular BDNF content was analyzed by immunostaining. In wild-type cultures, stimulation with 100 μm ATP induced a reduction of intracellular BDNF staining that was more pronounced in the presence of 3 μm ivermectin (IVM), a positive allosteric modulator of P2X4R (Fig. 4A). In contrast, in cultures from P2X4−/− mice, neither ATP nor ATP+IVM stimulations produced an alteration of intracellular BDNF content. These results were obtained using two different commercial anti-BDNF antibodies (data not shown). Corroborating observations were made when BDNF cellular content was analyzed by Western blotting (Fig. 4B). P2X4R-mediated BDNF release was also tested in a recombinant system. COS-7 cells were transfected with P2X4R and BDNF-GFP cDNAs either alone or in combination. Cells were stimulated by ATP+IVM and both cellular and secreted BDNF-GFP content analyzed by Western blotting. When P2X4 and BDNF-GFP were coexpressed, ATP+IVM induced a marked decrease of intracellular BDNF content (Fig. 4C); conversely, secretion of BDNF-GFP in the medium was increased (Fig. 4D). In addition, omitting calcium from the extracellular medium abolished ATP-mediated BDNF release.
Figure 4.
P2X4 stimulation triggers BDNF release from activated microglia. A, ATP-evoked release of BDNF from wild-type and P2X4−/− microglia primary cultures. Intracellular BDNF content of microglia was analyzed by immunostaining. Stimulation of a culture with ATP (100 μm) alone or coapplied with ivermectin (IVM, 3 μm) induced a strong decrease of BDNF immunoreactivity in a primary microglial culture from wild-type mice. In a culture from P2X4−/− mice, ATP or ATP+IVM stimulation did not induce any detectable changes in BDNF immunoreactivity. The data shown are representative of six experiments. Scale bar, 100 μm. B, Western blot of intracellular BDNF content from primary cultures of wild-type and P2X4−/− microglia. Cells were stimulated as above. The top band corresponds to pro-BDNF; the mature form (i.e., the 14 kDa form) could not be resolved in these experiments. ATP+IVM stimulation induced a reduction of intracellular pro-BDNF in wild-type but not in P2X4−/− cultures. The intermediate form seen in stimulated P2X4−/− cultures is of unknown origin. C, D, P2X4 activation triggered BDNF release in a recombinant expression system. P2X4 and BDNF-GFP cDNAs were transiently transfected in COS-7 cells either alone or in combination. Forty-eight hours later, cells were stimulated or not with ATP+IVM and intracellular (C) or secreted (D) BDNF-GFP was analyzed by Western blotting. Note that in the absence of extracellular Ca2+, ATP-induced secretion of BDNF was strongly reduced.
Discussion
Purinergic signaling appears to be a key pathway regulating microglial response to injury and nerve degeneration (Färber and Kettenmann, 2006). In this study using we show that in wild-type mice, PNI induces a strong upregulation of P2X4R expression in the spinal cord ispsilateral to the lesion, whereas it is barely detectable in sham animals. In line with previous studies (for review, see Inoue, 2006; Scholz and Woolf, 2007), our experiments performed in the CX3CR1+/GFP mice confirm that peripheral nerve injury induces activation of spinal microglia that is characterized by typical morphological changes. In addition, our results provide clear evidence that the induction of P2X4 expression in the spinal cord resulting from peripheral nerve lesion is restricted to activated microglia.
ATP released from damaged cells has been proposed to be a triggering factor of microglial activation (Inoue, 2002). However, in P2X4-deficient mice microglial activation subsequent to PNI is not affected. Indeed, morphological changes and P2X7 expression, both of which are associated with microglial activation, were unaffected in P2X4−/− mice. Interestingly, PNI-mediated transcriptional upregulation of P2X4 gene was still observed in KO mice. These observations therefore rule out a possible involvement of P2X4R in ATP-mediated microglial activation. Rather they suggest that within the CNS, P2X4 expression could represent a physiological marker of microglial activation.
P2X4R deletion results in a complete absence of mechanical hypersensitivity subsequent to peripheral nerve lesion, while leaving motor coordination untouched. We also provide evidence that tactile allodynia is reduced in P2X4−/− mice after spared nerve injury, a different model of neuropathic pain (supplemental Fig. 1, available at www.jneurosci.org as supplemental material). These behavioral phenotypes are in agreement with a previous study using intrathecal injections of P2X4R antisense oligonucleotides into rat spinal cord before PNI (Tsuda et al., 2003) and further demonstrate the direct involvement of microglial P2X4R in the establishment of mechanical hypersensitivity associated with neuropathic pain.
After PNI, ATP-mediated BDNF release from activated microglia likely mediates the downregulation of the K+/Cl− cotransporter KCC2 in inhibitory interneurons, which in turn gates allodynia (Coull et al., 2003, 2005). Our results provide a direct demonstration that P2X4R controls the release of BDNF from activated microglia subsequent to peripheral nerve damage. This conclusion is provided by our findings that in P2X4-deficient mice, nerve injury results in BDNF accumulation in dorsal horn microglia whereas phosphorylation of the NR1 subunit of the NMDA receptor is strongly decreased. This reduction of p-NR1 levels in dorsal horn neurons of P2X4R deficient mice may also account for the lack of hypersensitivity after PNI, suggesting that P2X4R-induced BDNF release from microglia not only promotes allodynia but may also contribute to longer term enhancement of synaptic strength (Kerr et al., 1999). Finally, using primary microglia cultures and a recombinant expression system, our results clearly demonstrate the direct involvement of P2X4R in ATP-mediated BDNF.
This work and recent studies highlight the roles of purinergic P2 receptors as critical regulators of microglial functions. In homeostatic brain, metabotropic P2Y12 receptors regulates microglial branch dynamics (Davalos et al., 2005), whereas in activated states P2X4, P2X7, P2Y12 or P2Y6 receptors are involved in the secretion of proinflammatory mediators, chemotaxis or in phagocytosis (Kettenmann, 2007). These studies also support the idea that purinergic signaling is central to bidirectional communications between microglia and other brain cells. Indeed, microglia, in either resting or activated states, can sense ATP released by local network activity through an array of purinergic receptors, which expression profile depends on activation states. There is now a growing number of evidence suggesting that activation of these receptors, particularly P2X4 and P2X7, can promote neuronal excitability. This is of particular importance in chronic brain disease at which sustained activation of these microglial receptors can promote long term modifications of synaptic strength or excitotoxic damages (Färber and Kettenmann, 2006). Targeting these receptors may well represent an attractive therapeutic alternative to NSAID treatment of chronic pain syndromes and/or to limit some deleterious effect of inflammation associated with neurodegenerative diseases.
Footnotes
This work was supported by the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique, the Agence Nationale de la Recherche (ANR-05-NEUR-037), the Association pour la Recherche sur le Cancer, and l'Institut UPSA de la Douleur. This work was made possible thanks to the Animal facility of Institut Fédératif de Recherche 3 and the Montpellier Réseau Inter-Organisme Imaging facility. We thank Claire Berthoud for her help with the spared nerve injury model.
References
- Biber K, Neumann H, Inoue K, Boddeke HW. Neuronal ‘On’ and ‘Off’ signals control microglia. Trends Neurosci. 2007;30:596–602. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2007.08.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buell G, Michel AD, Lewis C, Collo G, Humphrey PP, Surprenant A. P2X1 receptor activation in HL60 cells. Blood. 1996;87:2659–2664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G. Physiology and pathophysiology of purinergic neurotransmission. Physiol Rev. 2007;87:659–797. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00043.2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chessell IP, Hatcher JP, Bountra C, Michel AD, Hughes JP, Green P, Egerton J, Murfin M, Richardson J, Peck WL, Grahames CB, Casula MA, Yiangou Y, Birch R, Anand P, Buell GN. Disruption of the P2X7 purinoceptor gene abolishes chronic inflammatory and neuropathic pain. Pain. 2005;114:386–396. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2005.01.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coull JA, Boudreau D, Bachand K, Prescott SA, Nault F, Sík A, De Koninck P, De Koninck Y. Trans-synaptic shift in anion gradient in spinal lamina I neurons as a mechanism of neuropathic pain. Nature. 2003;424:938–942. doi: 10.1038/nature01868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coull JA, Beggs S, Boudreau D, Boivin D, Tsuda M, Inoue K, Gravel C, Salter MW, De Koninck Y. BDNF from microglia causes the shift in neuronal anion gradient underlying neuropathic pain. Nature. 2005;438:1017–1021. doi: 10.1038/nature04223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davalos D, Grutzendler J, Yang G, Kim JV, Zuo Y, Jung S, Littman DR, Dustin ML, Gan WB. ATP mediates rapid microglial response to local brain injury in vivo. Nat Neurosci. 2005;8:752–758. doi: 10.1038/nn1472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Färber K, Kettenmann H. Purinergic signaling and microglia. Pflugers Arch. 2006;452:615–621. doi: 10.1007/s00424-006-0064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari D, Chiozzi P, Falzoni S, Hanau S, Di Virgilio F. Purinergic modulation of interleukin-1 beta release from microglial cells stimulated with bacterial endotoxin. J Exp Med. 1997;185:579–582. doi: 10.1084/jem.185.3.579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanisch UK, Kettenmann H. Microglia: active sensor and versatile effector cells in the normal and pathologic brain. Nat Neurosci. 2007;10:1387–1394. doi: 10.1038/nn1997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes SE, Hollopeter G, Yang G, Kurpius D, Dailey ME, Gan WB, Julius D. The P2Y12 receptor regulates microglial activation by extracellular nucleotides. Nat Neurosci. 2006;9:1512–1519. doi: 10.1038/nn1805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue K. Microglial activation by purines and pyrimidines. Glia. 2002;40:156–163. doi: 10.1002/glia.10150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue K. ATP receptors of microglia involved in pain. Novartis Found Symp. 2006;276:263–272. discussion 273–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung S, Aliberti J, Graemmel P, Sunshine MJ, Kreutzberg GW, Sher A, Littman DR. Analysis of fractalkine receptor CX(3)CR1 function by targeted deletion and green fluorescent protein reporter gene insertion. Mol Cell Biol. 2000;20:4106–4114. doi: 10.1128/mcb.20.11.4106-4114.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr BJ, Bradbury EJ, Bennett DL, Trivedi PM, Dassan P, French J, Shelton DB, McMahon SB, Thompson SW. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor modulates nociceptive sensory inputs and NMDA-evoked responses in the rat spinal cord. J Neurosci. 1999;19:5138–5148. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-12-05138.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettenmann H. Neuroscience: the brain's garbage men. Nature. 2007;446:987–989. doi: 10.1038/nature05713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khakh BS, North RA. P2X receptors as cell-surface ATP sensors in health and disease. Nature. 2006;442:527–532. doi: 10.1038/nature04886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koizumi S, Shigemoto-Mogami Y, Nasu-Tada K, Shinozaki Y, Ohsawa K, Tsuda M, Joshi BV, Jacobson KA, Kohsaka S, Inoue K. UDP acting at P2Y6 receptors is a mediator of microglial phagocytosis. Nature. 2007;446:1091–1095. doi: 10.1038/nature05704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parvathenani LK, Tertyshnikova S, Greco CR, Roberts SB, Robertson B, Posmantur R. P2X7 mediates superoxide production in primary microglia and is up-regulated in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:13309–13317. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M209478200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubio ME, Soto F. Distinct Localization of P2X receptors at excitatory postsynaptic specializations. J Neurosci. 2001;21:641–653. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-02-00641.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholz J, Woolf CJ. The neuropathic pain triad: neurons, immune cells and glia. Nat Neurosci. 2007;10:1361–1368. doi: 10.1038/nn1992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seltzer Z, Dubner R, Shir Y. A novel behavioral model of neuropathic pain disorders produced in rats by partial sciatic nerve injury. Pain. 1990;43:205–218. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(90)91074-S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sim JA, Chaumont S, Jo J, Ulmann L, Young MT, Cho K, Buell G, North RA, Rassendren F. Altered hippocampal synaptic potentiation in P2X4 knock-out mice. J Neurosci. 2006;26:9006–9009. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2370-06.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sim JA, Park CK, Oh SB, Evans RJ, North RA. P2X1 and P2X4 receptor currents in mouse macrophages. Br J Pharmacol. 2007;152:1283–1290. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack SE, Pezet S, McMahon SB, Thompson SW, Malcangio M. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor induces NMDA receptor subunit one phosphorylation via ERK and PKC in the rat spinal cord. Eur J Neurosci. 2004;20:1769–1778. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2004.03656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda M, Shigemoto-Mogami Y, Koizumi S, Mizokoshi A, Kohsaka S, Salter MW, Inoue K. P2X4 receptors induced in spinal microglia gate tactile allodynia after nerve injury. Nature. 2003;424:778–783. doi: 10.1038/nature01786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L, Jacobsen SE, Bengtsson A, Erlinge D. P2 receptor mRNA expression profiles in human lymphocytes, monocytes and CD34+ stem and progenitor cells. BMC Immunol. 2004;5:16. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-5-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Z, Artelt M, Burnet M, Trautmann K, Schluesener HJ. Lesional accumulation of P2X4 receptor+ monocytes following experimental traumatic brain injury. Exp Neurol. 2006;197:252–257. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2005.09.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]