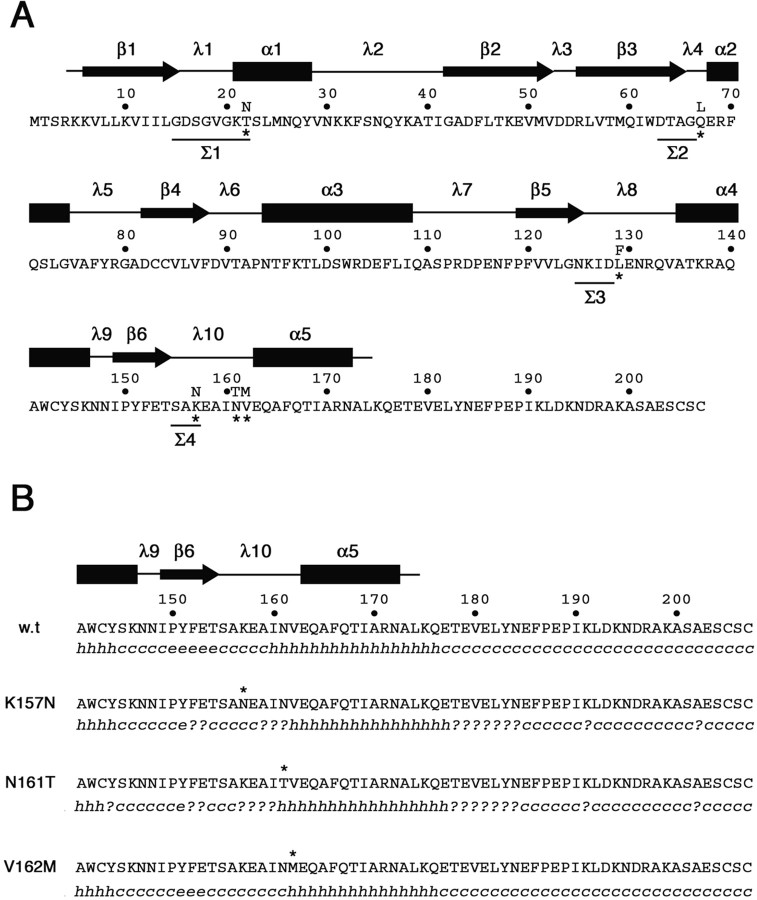
Figure 10.
Amino acid sequence and secondary structure of wild-type and CMT2B-associated Rab7 proteins. A, Amino acid sequence of the human wild-type Rab7 protein. Asterisks mark the amino acid substitutions in the mutated proteins Rab7 T22N, Rab7 Q67L, Rab7 L129F, Rab7 K157N, N161T, and V162M. Amino acids in the four sequence motifs (Σ1–Σ4) conserved in all GTP-binding proteins are underlined. Secondary structure above the amino acid sequence has been predicted on the basis of the available structural data for Rab proteins (Merithew et al., 2001). α1–α5, α helices; β1–β6, β sheets; λ1–λ10, loops. B, Secondary structure prediction in the C-terminal region of wild-type and CMT2B-associated Rab7 proteins. The software Secondary Structure Prediction at the Pôle Bioinformatique Lyonnais (http://pbil.univ-lyon1.fr/) has been used with the methods DSC, MLRC, and PHD (with default parameters) that generated the secondary consensus shown below each amino acid sequence. h, α helix; e, extended strand; c, random coil; ?, ambiguous state.