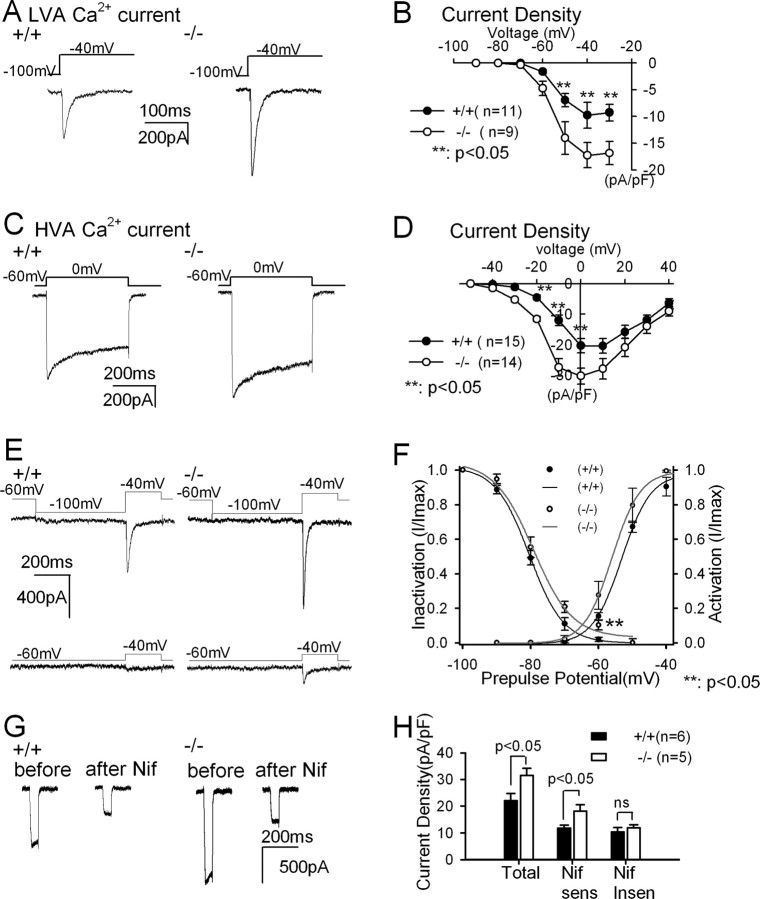
Figure 3.
Enhanced LVA and HVA Ca2+ currents in PLCβ4−/− TC neurons. LVA (A) and HVA (C) Ca2+ currents were measured from wild-type and PLCβ4−/− TC neurons. I–V relationships of the LVA Ca2+ current density (B) and of the HVA Ca2+ current density (D) in wild-type (filled circles) and PLCβ4−/− (open circles) TC neurons revealed the increased LVA and HVA Ca2+ currents in PLCβ4−/− TC neurons. E, LVA Ca2+ currents from wild-type (left) and PLCβ4−/− (right) TC neurons activated by voltage steps from −100 to −40 mV (top) and from −60 to −40 mV (bottom). F, Steady-state inactivation curves and activation curves for LVA Ca2+ currents in wild-type (filled circles and black lines) and PLCβ4−/− TC neurons (open circles and gray lines) showed that less steady-state inactivation of LVA Ca2+ currents increased the window currents in PLCβ4−/− TC neurons. Ca2+ currents were measured with activation steps to −40 mV from the given prepulse potentials ranged from −100 to −50 mV. Degree of inactivation was measured as the ratio of current density at given prepulse potential divided by maximum current density measured at −100 mV prepulse. Activation curves were obtained from Ca2+ currents measured when the membrane potential was hyperpolarized to −100 mV followed by the activation steps ranged from −90 to −40 mV. Smooth curves represent fits to the data with a Boltzmann equation. G, HVA Ca2+ current was measured in voltage steps from −60 to 0 mV before and after 10 μm nifedipine (Nif) treatment, in wild-type (left) and PLCβ4−/− (right) TC neurons. H, Current density of total, nifedipine-sensitive and nifedipine-insensitive HVA Ca2+ currents.