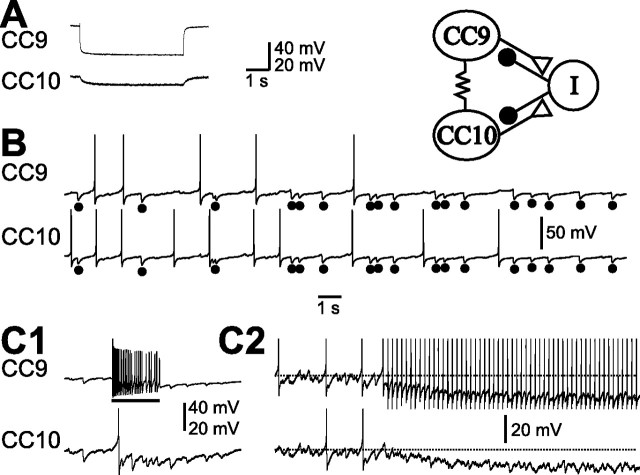
Figure 2.
Electrophysiological characteristics of CC9/10. A, CC9 is electrically coupled to CC10. Injection of negative current into CC9 hyperpolarized CC10. B, CC9 and CC10 were spontaneously active, and individual spontaneous IPSPs (dots) were mostly coincident. C, DC stimulation of CC9 (bar) increased the frequency of occurrence of IPSPs in CC10 (C1). Stimulation of CC9 with short current pulses at 5 Hz induced feedforward inhibition in CC10 and a feedback inhibition in CC9 itself (C2), likely mediated by the “I” cell (schematic diagram at top right). Horizontal dotted lines indicate approximate resting membrane potentials. Synaptic connections are summarized in the schematic diagram (top right). Polysynaptic inhibition of both CC9 and CC10 is hypothesized to be mediated by an as yet unidentified inhibitory interneuron “I.” Recordings in A were made in high-divalent saline, all other recordings were made in normal seawater.