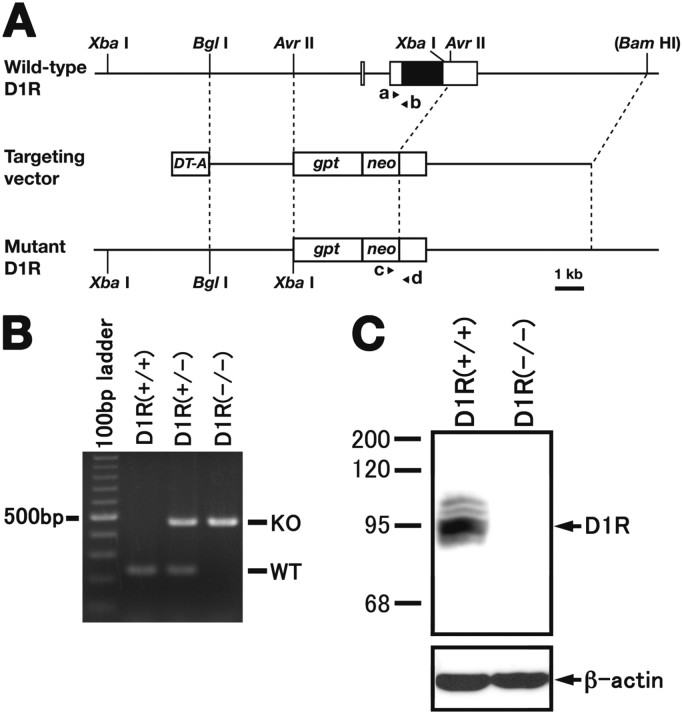
Figure 1.
Generation of the D1R-KO mice and expression of the D1R protein in the brains of WT and D1R-KO mice. A, Schematic representation of the WT allele, the targeting vector, and the mutant allele of the mouse D1R gene. The coding and untranslated regions are shown as closed and open boxes, respectively. Primers for PCR genotyping (primers a, b, c, and d) are shown as small arrowheads indicated by a, b, c, and d, respectively. A BamHI site is indicated with parentheses when relevant. The diphtheria toxin A subunit (DT-A), E. coli xanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase (gpt) and neomycin resistant (neo) genes are shown as open boxes. B, PCR genotyping of wild-type (D1R+/+), heterozygous (D1R+/−), and homozygous (D1R−/−) mutant mice. PCR products from the WT allele and the mutant (KO) are 234 bp and 460 bp, respectively. C, Western blot using a D1R-specific antibody revealed that D1R protein was completely absent from D1R−/− mice.