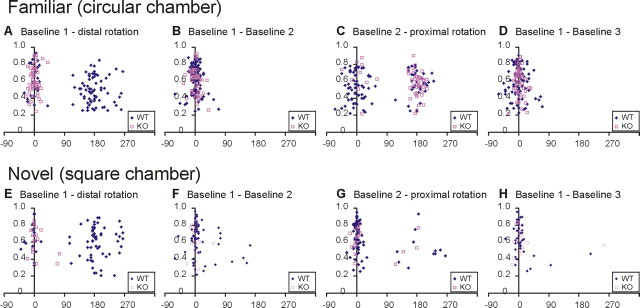
Figure 7.
Scatterplots of spatial correlation values versus rotation angles that produced maximal correlation values between pairs of sessions for hippocampal place cells in WT and D1R-KO mice. Rotation angles are represented on the abscissa, and spatial correlation values between pairs of sessions are represented on the ordinate; blue filled diamonds are for WT mice, and red open squares for D1R-KO mice. A–D, In the familiar environment, there were two subpopulations of place cells in WT mice in which the place fields were influenced by distal cues (distributed around 180°, standard session vs distal rotation session) (A) and proximal cues (distributed around 180°, baseline session 2 vs proximal rotation session) (C), with the influence of the distal cues predominant over the proximal cues. For D1R-KO mice, no place cells shifted their place fields by rotation of the distal cues (all around 0°) (A), and most cells shifted their place fields by rotation of the proximal cues (C). E–H, In the novel environment, the predominant effect of the distal cues (E) over proximal cues (G) was still seen and was more pronounced in WT mice. In D1R-KO mice, only a few cells responded to the rotation of the distal cues (E) and proximal cues (G), and many cells did not follow distal or proximal cue changes in the novel environment.