Figure 2.
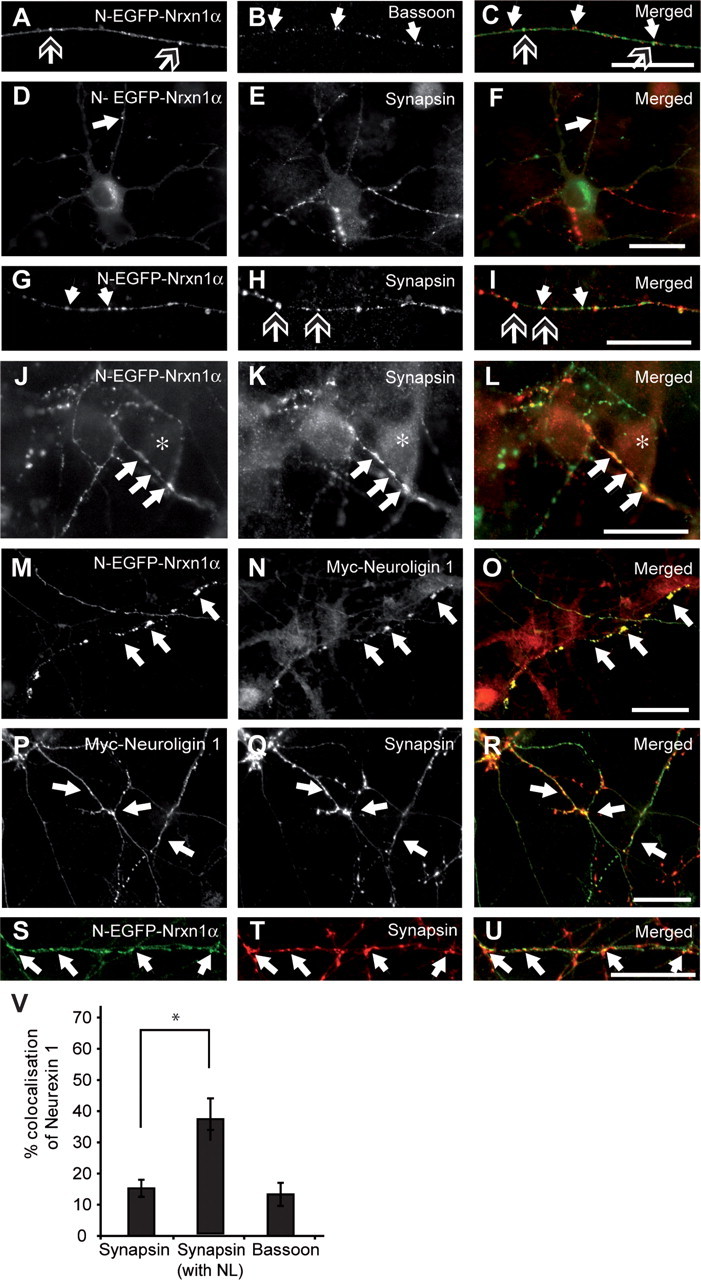
EGFP-tagged Nrxn1α is recruited to synapses. Nrxn1α-transfected neurons (A, C, D, F, G, I, J, L, M, O, S, U; green in merged pictures) were colabeled with antibodies against bassoon (B, C) or synapsin (E, F, H, I, K, L; red in merged pictures). Alternatively, neurons were cotransfected with both N-EGFP-Nrxn1α and myc-tagged neuroligin 1, and labeled for neuroligin (N, O) or synapsin (Q, R, T, U). A–C, Tagged Nrxn1α (open-headed arrows) does not colocalize with bassoon (white arrows) along the length of axons. D–I, Tagged Nrxn1α (white arrows) does not colocalize with synapsin (open-headed arrows) in intracellular puncta along the axon (D–F), but colocalization is observed at presumed synaptic contact sites (G–I). J–L, Asterisks denote the soma of a neighboring neuron, over which an axon with Nrxn1α-positive puncta is positioned, resulting in colocalization between synapsin (K) with Nrxn1α (J, L; white arrows). M–U, Inducing presynaptic differentiation by cotransfecting neuroligin 1 results in enlarged Nrxn-positive clusters (M, O; white arrows) colocalizing with neuroligin 1 (N, O), and synapsin (S–U, white arrows). V, Quantification of colocalization between Nrxn1α and synapsin or bassoon. *p < 0.05; scale bars, 40 μm.
