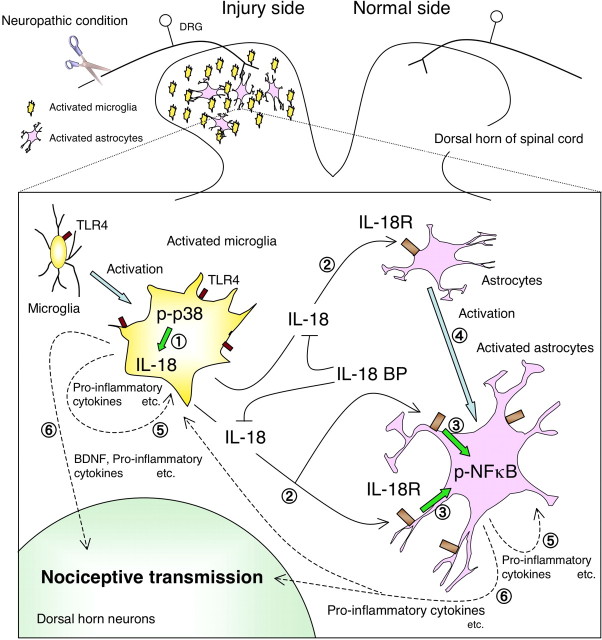
Figure 12.
Proposed model of IL-18-mediated microglia/astrocyte interaction in the spinal cord. First, TLR4 triggers microglial activation through the p38 MAPK pathway  . IL-18 produced by the TLR4/p38 MAPK signaling cascade in activated microglia stimulates IL-18R on astrocytes in a paracrine manner
. IL-18 produced by the TLR4/p38 MAPK signaling cascade in activated microglia stimulates IL-18R on astrocytes in a paracrine manner  . IL-18 binding to IL-18R increases NFkB phosphorylation in astrocytes and causes GFAP upregulation
. IL-18 binding to IL-18R increases NFkB phosphorylation in astrocytes and causes GFAP upregulation  . IL-18R expression is upregulated by IL-18R stimulation, thus accelerating this signaling pathway in astrocytes
. IL-18R expression is upregulated by IL-18R stimulation, thus accelerating this signaling pathway in astrocytes  . IL-18 or other cytokines might stimulate microglia and astrocytes in an autocrine or paracrine manner and induce production of pro-inflammatory molecules, such as IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α, as well as COX-2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase
. IL-18 or other cytokines might stimulate microglia and astrocytes in an autocrine or paracrine manner and induce production of pro-inflammatory molecules, such as IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α, as well as COX-2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase  . These pro-inflammatory molecules induced in glial cells sensitize dorsal horn neurons in the spinal cord
. These pro-inflammatory molecules induced in glial cells sensitize dorsal horn neurons in the spinal cord  .
.