Figure 6.
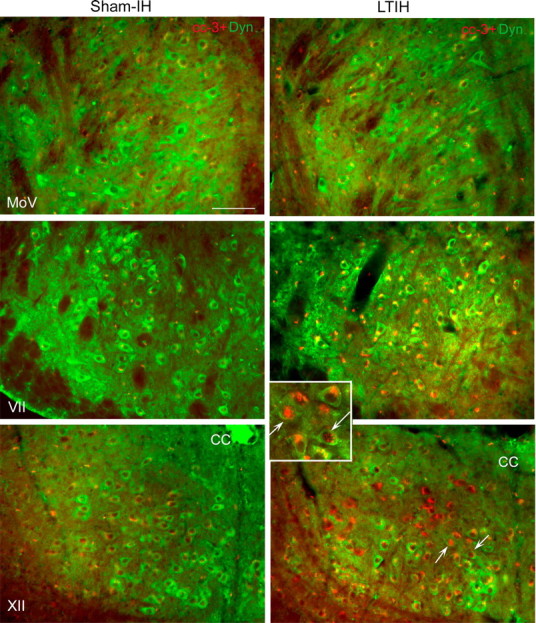
LTIH increase in cC-3 immunoreactivity in both facial and hypoglossal but not in motor trigeminal neurons. Low-power fluorescence photomicrographs of cC-3 (Alexa Fluor 594; red color) with dynactin-1/p150glued (Alexa Fluor 488; green color) in facial, hypoglossal, and trigeminal neurons are shown to illustrate heterogeneities in cC-3 immunoreactivities across motor nuclei groups and within motor nuclei. Overall, cC-3 immunoreactivity followed the LTIH cC-7 response (as shown in Fig. 5) with the majority of cC-3 localized to the perinuclear envelope in hypoglossal and facial motoneurons, and only rare nuclear translocation. A small percentage of hypoglossal and facial motoneurons revealed nuclear translocation of cC-3 in response to LTIH (arrows, inset box for LTIH XII). Minimal cC-3 was observed in sham-LTIH motoneurons in all three motor nuclei studied and motor trigeminal neurons in mice exposed to LTIH. Scale bar, 100 mm.
