Fig. 3.
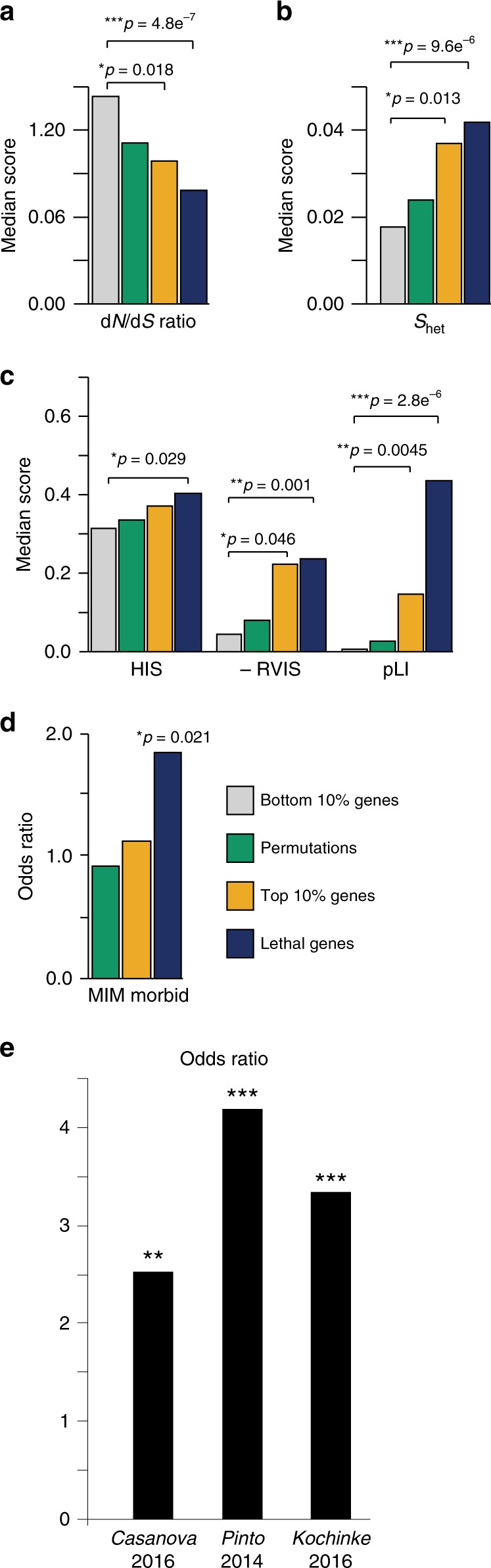
Predicted gene deleteriousness in humans. a Mouse lethal genes51 and the top 10% of mutants with the largest neuroanatomical abnormalities are compared to the bottom 10% and to randomly permuted sets of these genes. The dN/dS ratio examines selection pressures by comparing the rate of synonymous and non-synonymous substitutions. b, c Comparison of the gene properties of the human orthologs of lethal genes51 and of the top 10% of mutants with the largest neuroanatomical abnormalities as compared to genes in the bottom 10% and to randomly permuted sets of these genes. shet (Selection coefficient associated with the loss of heterozygosity), RVIS (Residual Variation Intolerance Score), and pLI (probability of being Loss of function Intolerant) are all indicators of purifying selection pressure, while HIS are predicted HaploInsufficiency Scores (Supplementary Notes). d The overlap between gene sets from A and B with MIM Morbid Map genes. e Enrichments of intellectual disability-associated genes from three independent publications and developmental disorder-associated genes (Supplementary Notes) among human orthologs of NeuroAnatomical Phenotype (NAP) genes compared to human orthologs of non-NAP. *0.05 < p < 0.01; **0.01 < p < 0.001; ***p < 0.001 (right-tailed Mann–Whitney U test for a–d and right-tailed Fisher’s test for e)
