Figure 13.
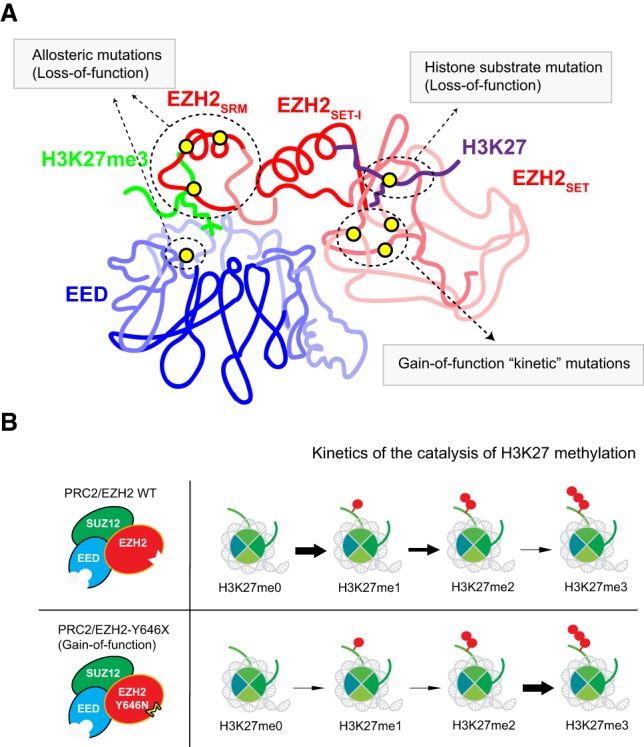
Mutations of PRC2 and its substrate in cancer. (A) Major groups of mutations that influence PRC2 function in cancer. Mutations that are found in the EED cage (EED I363M) (Ueda et al. 2016) and SRM domain of EZH2 (P132S, D142V, and F145L) inhibit allosteric activation of PRC2 (Lee et al. 2018c). Mutations that are found in the catalytic SET domain (Y646X [X = S, N, F, C, or H], A682G, A682V, and A692V) are gain-of-function “kinetic” mutations. Histone H3K27M is a dominant-negative substrate mutation that globally inhibits PRC2 activity. (B) Illustration depicting the kinetics of catalysis of each H3K27 methylation state. EZH2 mutants in Y646 specifically promote the catalysis of H3K27me3 from H3K27me2 but dampen catalysis of the lower methylation states.
