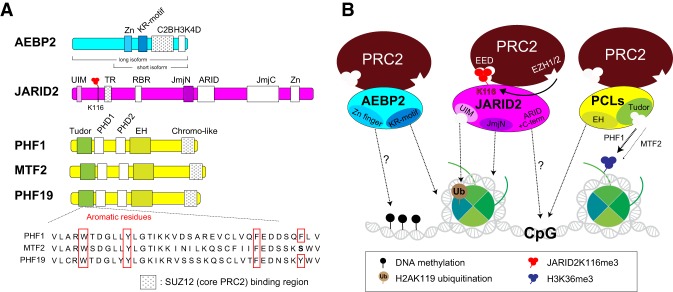
Figure 5.
Biochemical characterization of PRC2 accessory factors. (A) Domains within PRC2 accessory proteins are indicated. SUZ12 binding domains are highlighted by gray dots. (Bottom) Sequence alignment of the Tudor domains within three mammalian PCL proteins. The critical aromatic residues that can form a cage are highlighted by red squares. The cage within the PCLtudor are bound to H3K36me3 (and, to a lesser extent, H3K36me2) in vitro. (B) PRC2 accessory proteins regulate its activity through several means: increasing its affinity for nucleosome binding (e.g., AEBP2KR motif and JARID2JmjN) and DNA (e.g., AEBP2Zn, JARID2C-term, and PCLEH), interacting with histone posttranslational modifications (hPTMs) (e.g., JARID2UIM [H2AK119ub] and PCLTudor [H3K36me2/me3]), and/or regulating its allosteric activation (e.g., JARID2-K116me3). (C2B) C2-binding domain; (TR) transrepression; (RBR) RNA-binding region; (JmjN) Jumonji N; (JmjC) Jumonji C; (PHD1/2): plant homeodomain 1/2.