Figure 4.
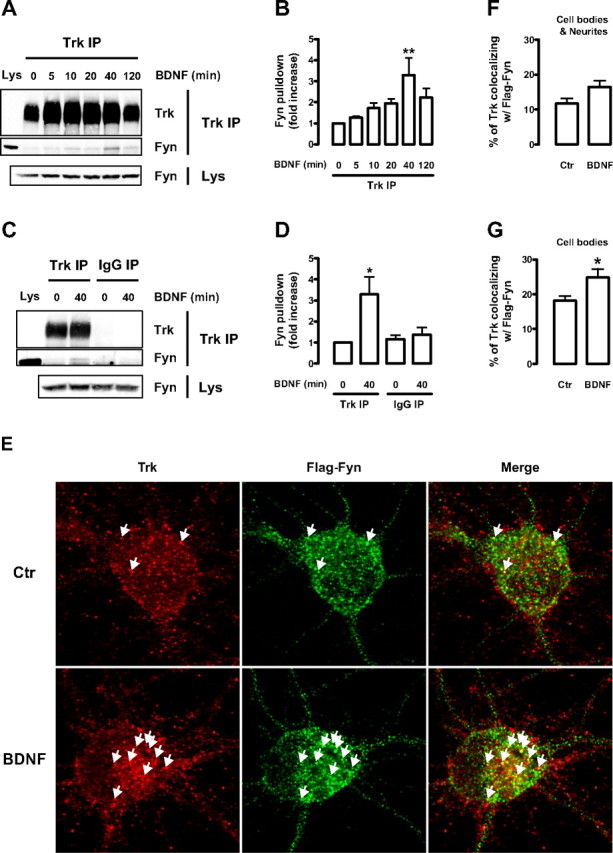
BDNF induces endogenous Trk–Fyn association and increases the colocalization of Trk and Flag–Fyn in cultured cortical neurons. A–D, Lysates obtained from DIV 9 rat cortical neurons, stimulated with BDNF for the indicated periods of time, were immunoprecipitated with anti-Trk (C-14) antibody (Trk IP) (A) or with normal rabbit IgG (IgG IP) (B). The immunoprecipitates were probed with anti-Trk (C-14) (1:100) and anti-Fyn (15) antibodies. A sample of whole lysate (Lys) was run side by side with the immunoprecipitates. As a loading control, the amount of Fyn present in the whole lysates is shown at the bottom. Quantitative analysis of coimmunoprecipitated Fyn from the experiments depicted in A and B are shown in C and D, respectively. Data are presented as mean fold increase ± SEM of three to five independent experiments. The indicated conditions are statistically different from the unstimulated control (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01). E, Immunocytochemistry of control (Ctr) and BDNF-stimulated DIV 9 rat cortical neurons transfected with Flag–Fyn at DIV 6. Cells were double stained with anti-Trk (C-14) and anti-Flag antibodies. Arrows depict colocalization between green and red puncta. F, G, Quantification of the percentage of Trk that colocalizes with Flag–Fyn. Colocalization was assessed in a region of interest that contained the whole cell (cell bodies and neurites; F) or just the cell body (G) of Flag–Fyn-positive neurons. Results are expressed as mean percentage ± SEM for six independent experiments, in which ∼8–12 cells per condition per experiment were imaged. The indicated condition is statistically different from the control as determined by unpaired two-tailed t test (*p < 0.05).
