Figure 6.
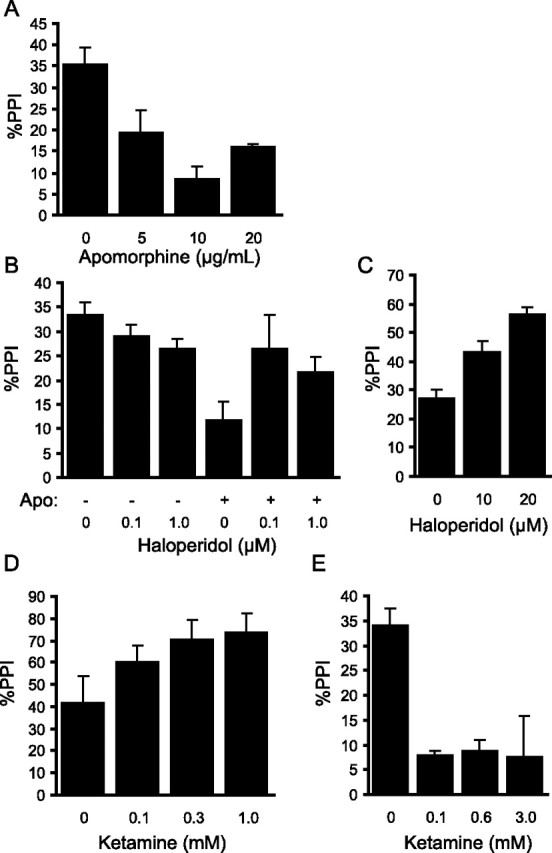
Dopaminergic and glutamatergic drugs modulate PPI in larval zebrafish. A, The mixed D1/D2 agonist apomorphine suppresses PPI in 6 dpf zebrafish larvae when added to the medium 10 min before testing (F(3,13) = 10.3; p = 9.6 × 10−4; n = 4 for each group except control, n = 5). B, Pretreatment of larva, 20 min before testing, with either 0.1 or 1.0 μm of the D2 antagonist haloperidol has no significant effect on PPI, but does block the disruption of PPI by apomorphine (two-factor ANOVA gives significant apomorphine by haloperidol interaction, F(2,35) = 3.3, p = 0.03; n = 6 for each group). C, At higher concentrations (10 and 20 μm), haloperidol enhances baseline PPI (F(2,21) = 21.8; p = 7.6 × 10−6; n = 8, each group). D, The NMDA receptor antagonist ketamine augments PPI when the prepulse is given 30 ms before the startle stimulus (F(3,22) = 15.5; p = 1.2 × 10−5; n = 6 for each group except control, n = 8). E, Ketamine disrupts PPI at 500 ms interstimulus interval (F(3,20) = 8.3; p = 8.7 × 10−4; n = 6, each group). Error bars indicate mean percent PPI ± SEM.
