Figure 10.
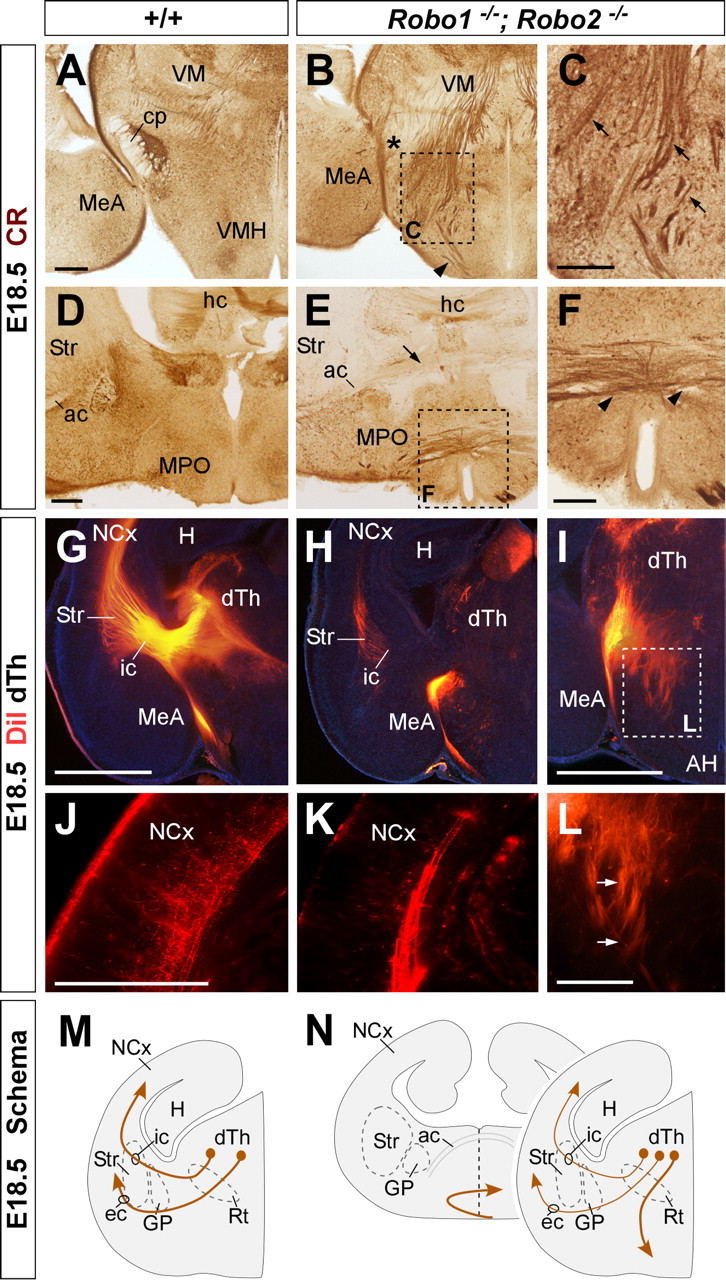
Thalamocortical axons follow abnormal paths in Robo1;Robo2 double-mutant mice. A–F, Coronal sections through the diencephalon of E18.5 fetuses showing calretinin immunohistochemistry in wild-type (A, D) and Robo1;Robo2 double-mutant mice (B, C, E, F). Note the abnormal invasion of thalamocortical fibers into the hypothalamus (C, arrows). At more rostral levels, thalamocortical axons cross the ventral midline (F, arrowheads) below the additional abnormal cross of corticofugal fibers (E, arrow). G–I, L, Coronal sections through the diencephalon of E18.5 embryos with DiI implanted in the dorsal thalamus (dTh), showing DiI axons abnormally entering the hypothalamus in Robo1;Robo2 double-mutant mice (H, I). J, K, Very few thalamic axons reach the cortex in Robo1;Robo2 double-mutant mice. M, N, The schemas summarize the pathways followed by thalamocortical axons in wild-type (M) and Robo1;Robo2 double-mutant mice (N). Str, Striatum; VMH, ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus; MeA, medial amygdala; cp, cerebral peduncle; ac, anterior commissure; ic, internal capsule; ec, external capsule; GP, globus pallidus; Rt, reticular thalamic nucleus; MPO, medial preoptic area; hc, hippocampal commissure; H, hippocampus, AH, anterior hypothalamus; VM, ventromedial nucleus. Scale bars: A, B, D, E, 300 μm; C, F, 200 μm; G–I, 1 mm; J–L, 200 μm.
