Figure 7.
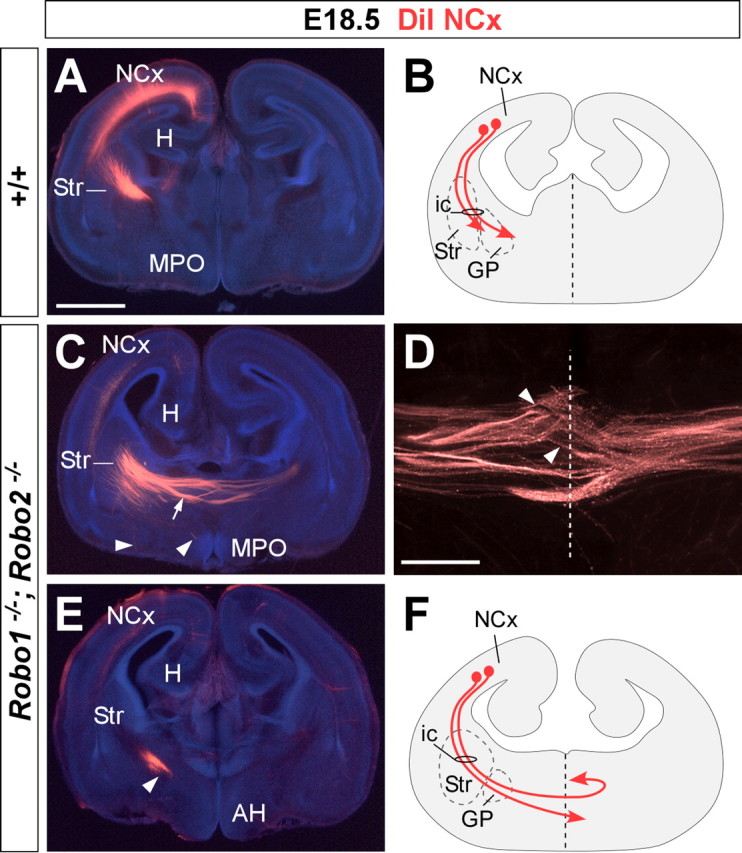
Corticofugal axons abnormally reach the telencephalic midline in Robo1;Robo2 double-mutant mice. Coronal sections through the telencephalon of E18.5 brains with DiI implanted in the neocortex (NCx), showing computer-generated overlays of DiI-labeled corticofugal axons and Hoechst counterstaining from wild-type (A) and Robo1;Robo2 mutants (C–E). The midline is indicated with a dotted line in D. The schemas summarize the results obtained in control (B) and Robo1;Robo2 mutants (F). A, B, In wild-type mice, labeled axons extend from the cortex into the striatum (Str). C–F, In Robo1;Robo2 mutants, labeled axons from the internal capsule (ic) abnormally approach the midline and cross it (C, arrow). A few axons that reach the midline course ventrally (arrowheads). Most of the axons that crossed the midline at more anterior levels were found in the contralateral side, where they either travel to the base of the telencephalon or extend toward the contralateral cortex (C, D). MPO, Medial preoptic area; H, hippocampus, AH, anterior hypothalamus. Scale bars: A, C, E, 1 mm; D, 300 μm.
