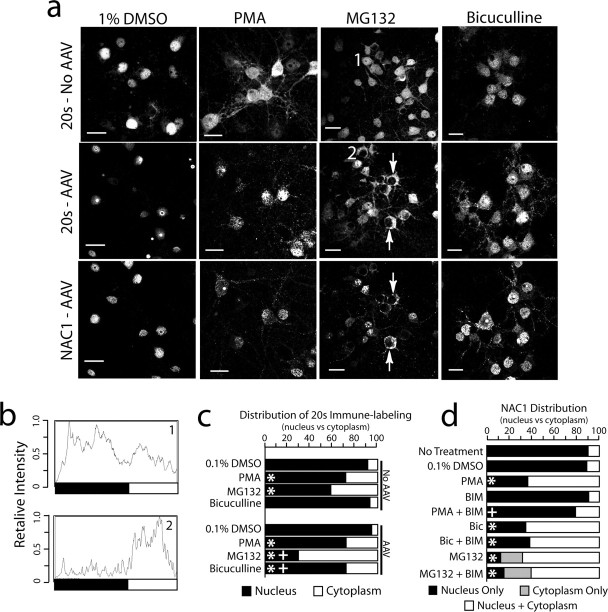
Figure 3.
Translocation of NAC1 and 20S from the nucleus to the cytoplasm and dendritic shaft. a, NAC1 and the 20S were translocated into the cytoplasm by MG132-induced inhibition of the proteasome (10 μm, 6 h), PMA-induced activation of PKC (10 μm, 1 h), or bicuculline disinhibition (40 μm, 2 h). DMSO was the control incubation (0.1%, 12 h). Neurons were either infected with AAV-NAC1 or not infected (No AAV). Arrows show cells with complete translocation of 20S and NAC1 from the nucleus to cytoplasm by MG132. Scale bars, 20 μm. b, Individual intensity plot of 20S cellular fluorescence corresponding to cells labeled 1 and 2 in a. c, Quantification of relative fluorescence of 20S in the nucleus versus cytoplasm after all treatments shown in a using relative intensity plots. Data were collected by an individual unaware of the treatment group and are shown as the mean proportion of fluorescence for n = 6–8 per treatment group. d, Quantification of the relative distribution of NAC1 labeling in the nucleus, nucleus and cytoplasm, and cytoplasm only (in the case of MG132, some cells had no measurable labeling in the nucleus). Quantification was made by an individual unaware of the treatment groups classify each cell in a culture dish (n = 6 dishes per treatment). For c and d, the data are presented as the mean proportion of fluorescence for n = 6–8 in each treatment group. *p < 0.05, compared with 0.1% DMSO using a Kruskal–Wallis test; +p < 0.05, comparing between treatments with or without AAV infection (c) or with or without BIM (d)