Figure 3.
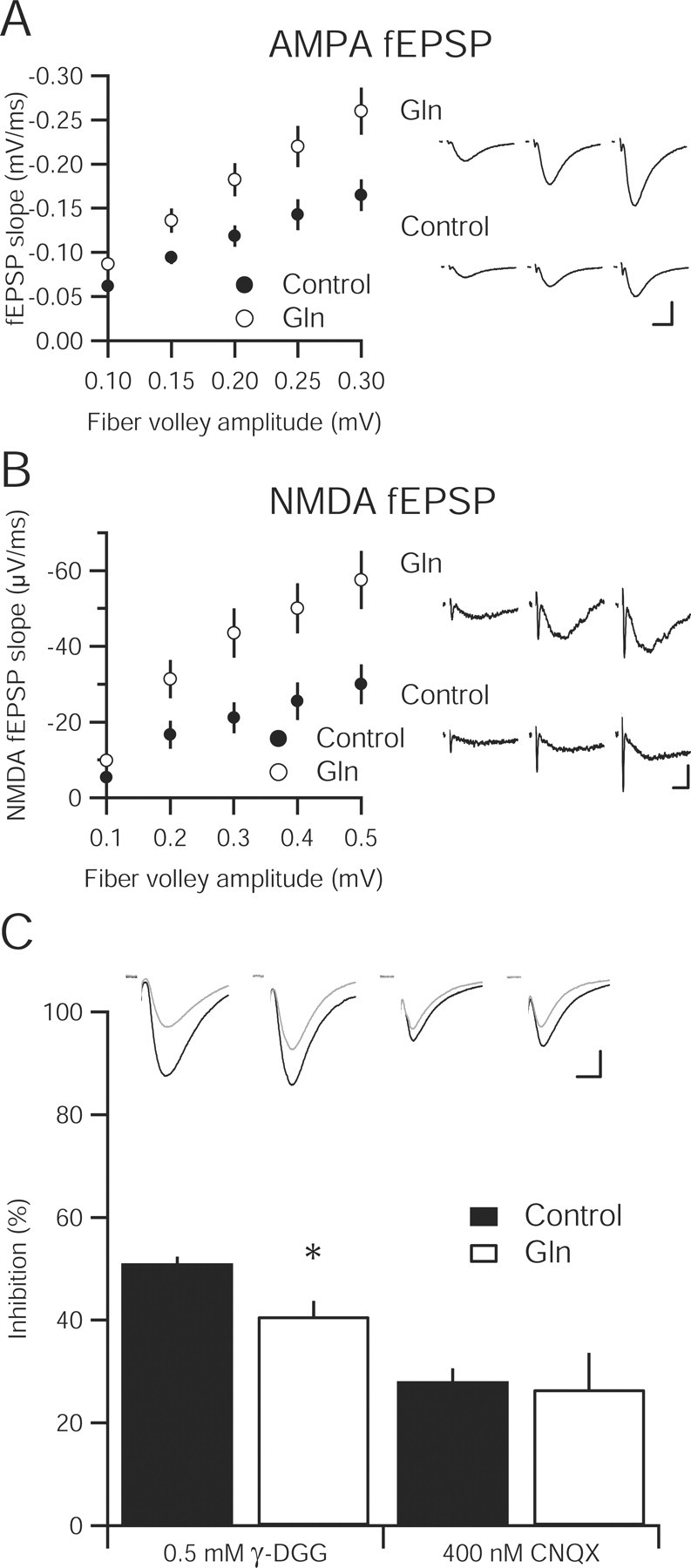
Increasing extracellular glutamine enhances synaptic transmission and vesicular glutamate content in hippocampal slice. A, Input–output relationship of the AMPA-mediated fEPSPs in hippocampal slices incubated in 4 mm glutamine (n = 16) compared with a 4 mm sucrose osmotic control (n = 15) are statistically greater at all fiber volley amplitudes (p < 0.05). Sample fEPSPs at different fiber volley amplitudes from each group are shown to the right. Calibration: 0.5 mV, 10 ms. B, Input–output curve of NMDA-mediated fEPSP in 4 mm glutamine-incubated slices (n = 13) is significantly enhanced over control slices (n = 12). Representative traces from three fiber volley amplitudes are shown to the right for glutamine-incubated (top) and control (bottom) slices. Calibration: 0.1 mV, 10 ms. C, Inhibition of evoked EPSCs by the low-affinity AMPA receptor antagonist γ-DGG (0.5 mm) is reduced in 4 mm glutamine-incubated slices (n = 12) relative to control (n = 10; * p < 0.05). However, the high-affinity antagonist CNQX (400 nm) produces similar inhibition in both control (n = 7) and glutamine-incubated slices (n = 6; p > 0.05). Inset, Sample traces before (black traces) and after (gray traces) γ-DGG and CNQX application. Calibration: 25 pA, 10 ms.
