Figure 5.
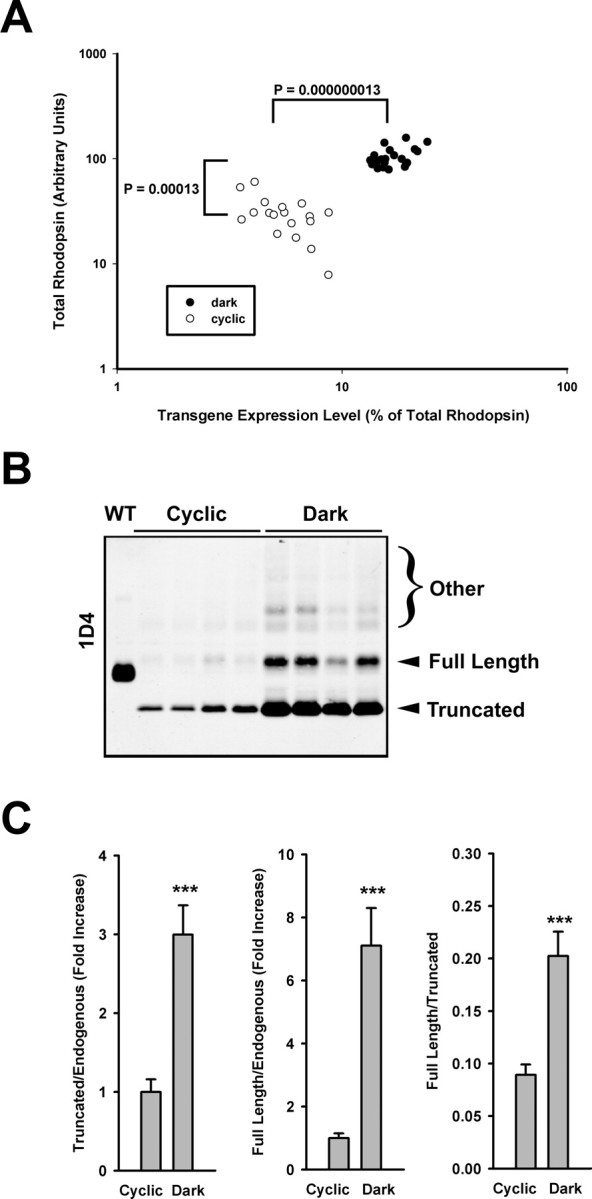
Dark rearing rescues RD in F1 transgenic animals expressing bovine P23H rhodopsin and is associated with an increase in P23H rhodopsin expression levels. A, Retinal extracts of G418-selected F1 offspring were subjected to dot-blot analysis using mAbs 1D4 and B6–30N (as described for Figs. 1 and 3), and total and percentage transgenic rhodopsin levels were similarly determined. Dark rearing rescued total rhodopsin levels in F1 offspring and also resulted in a significant increase in expression levels of the transgenic P23H rhodopsin. B, mAb 1D4 Western blot of samples from the same experiment demonstrating the dramatic increase in total bovine P23H rhodopsin under dark-rearing conditions, consisting primarily of the lower Mr cleaved form. Extracts of four representative eyes from each group are shown, as well as a control expressing wild-type bovine rhodopsin (wt). C, Bar graphs illustrate the differences in relative abundances of cleaved and full-length material (relative to endogenous mAb B630N reactive material and relative to each other) obtained from similar blots with additional samples (n = 14 for each group). All illustrated differences were statistically significant with p < 0.0001 (t test). Error bars are ±SEM.
