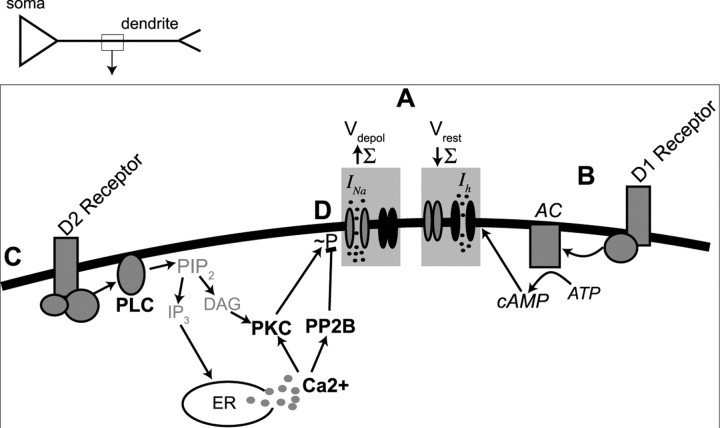
Figure 12.
Summary of the effects of DA on synaptic integration. A, DA exerts two primary actions on summation of PSPs: (1) increase in summation (Σ) at depolarized membrane potentials (Vdepol) by enhancement of Na currents, and (2) reduction in summation near Vrest by enhancement of h-currents. B, Activation of DA D1 receptors reduced summation near Vrest by a pathway dependent on adenylyl cyclase and cAMP (Rosenkranz and Johnston, 2006). C, Activation of DA D2 receptors increased summation by a pathway dependent on PLC, internal Ca2+, and PP2B. Blockade of PKC exerted an opposing influence, consistent with a D2-mediated enhancement of summation through reduction in Na-channel phosphorylation (∼P), which increases Na-channel activity. This, however, does not rule out other ion channels or signaling molecules in the actions of DA. Our data indicate that these are the most prominent signaling cascades and ion channels involved in the DAergic actions under these conditions. In addition, although our data are consistent with D2-mediated modulation of dendritic excitability, it is possible that this does not occur via modulation of Na+ channels and does not rule out potential involvement of D1 receptors. Signaling molecules in bold lettering indicate evidence from the current study. Signaling molecules in italics represent evidence from a previous study (Rosenkranz and Johnston, 2006). Gray lettering indicates signaling molecules that are known to usually be in that signaling cascade but that were not examined in this study. AC, Adenylyl cyclase; PIP2, phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate; IP3, inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate; DAG, diacylglycerol; ER, endoplasmic reticulum.