Figure 2.
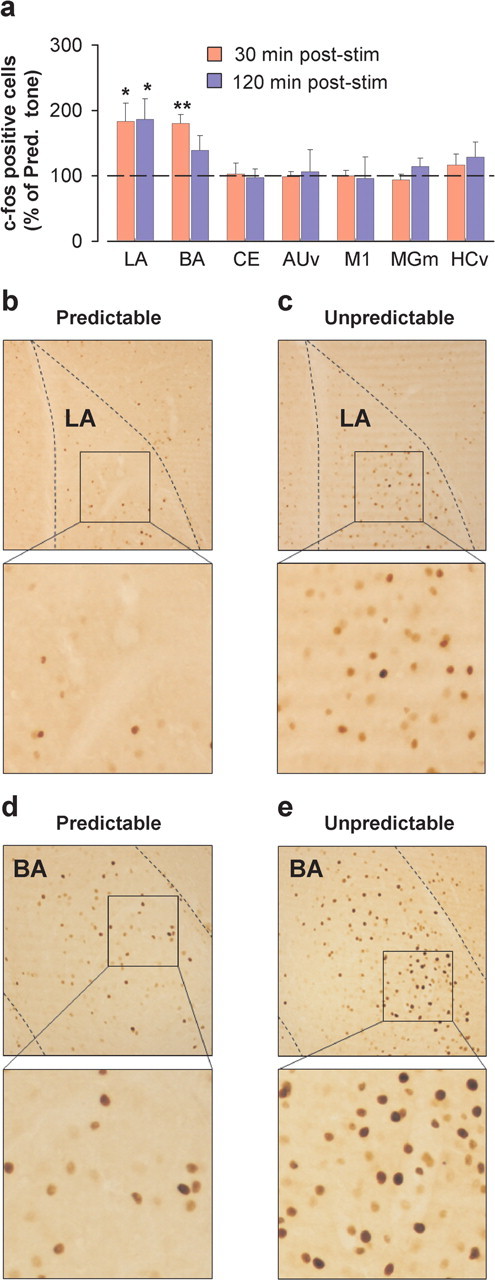
Increased c-Fos induction by unpredictably timed sound pulse stimulation in the lateral and basal amygdala. a, c-Fos induction in the LA, BA, and central (CE) nuclei of the amygdala, ventral auditory cortex (AUv), medial division of the medial geniculate nucleus of the thalamus (MGm), ventral hippocampus (HCv), and primary motor cortex (M1) quantified 30 min (n = 4–5 per group) and 120 min (n = 4–6 per group) after the start of unpredictably timed sound pulse stimulation (stim). Results are expressed as a percentage of the number of c-Fos-positive cells induced by predictably timed sound pulse stimulation (Pred. tone). All p < 0.05 (Scheffé's F test). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01. b, c, Photomicrographs illustrating increased c-Fos levels in the LA 120 min after the start of unpredictably versus predictably timed sound pulse stimulation. d, e, Photomicrographs illustrating increased c-Fos levels in the BA 30 min after the start of unpredictably versus predictably timed sound pulse stimulation.
