Figure 3.
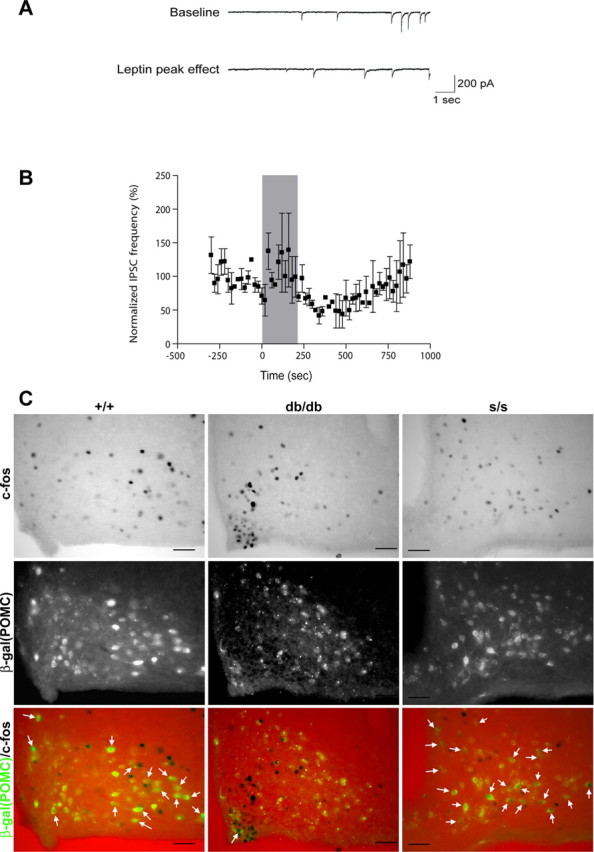
Leptin decreased the frequency of miniature IPSCs onto POMC neurons in s/s mice. A, Ten-second sweeps of raw synaptic data from a single POMC neuron showing baseline IPSCs 45 s before (top trace) and 306 s after (bottom trace) the start of leptin (100 nm) bath application. B, Leptin (100 nm) reversibly decreased the inhibitory synaptic input onto POMC neurons from s/s animals. The shaded region corresponds to time of drug application (n = 2). C, Representative images showing immunohistochemical detection of c-Fos (top, black nuclei) and immunofluorescent detection of β-Gal (middle, β-Gal/POMC, green) (bottom is merge) in db/db and s/s animals with β-Gal expression in POMC neurons (approximately bregma −1.9 mm). White arrows indicate colocalization of CFLIR with β-Gal; similar results were seen in multiple independent animals. Scale bars, 5μm.
