Figure 2.
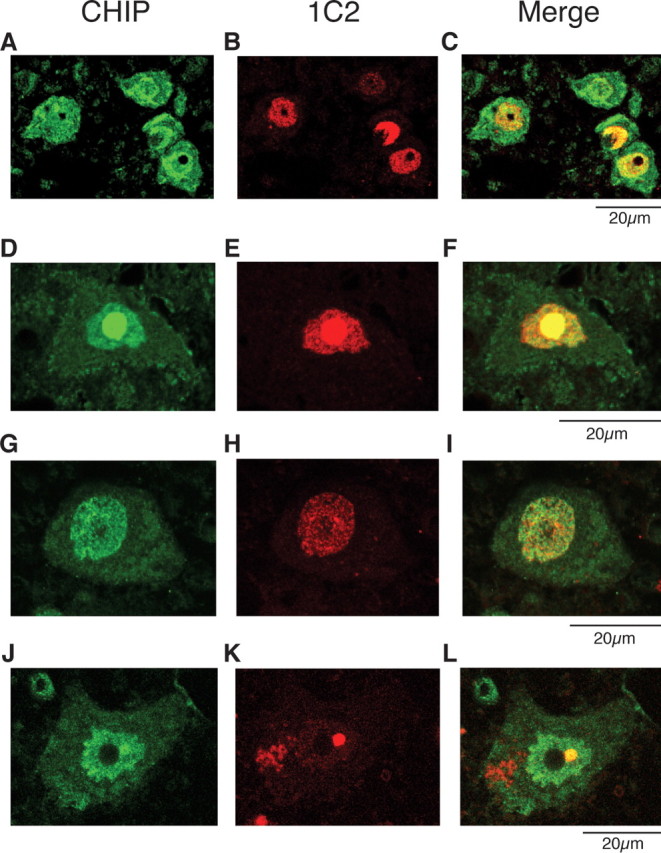
Colocalization of nuclear-localized CHIP with mutant AR. A–L, Anti-CHIP and anti-polyQ immunohistochemistry in spinal cords of 16-week-old AR-97Q mice (A–F) and an SBMA patient (G–L). A–C, Double-immunofluorescence staining for CHIP (A; green), expanded-polyQ (B; red), and overlay of the two signals (C; yellow) in the spinal anterior horn cells. D–F, CHIP (green; D) and mutant AR (red; E) are colocalized in nuclear inclusions (shown in yellow; F) in the spinal anterior horn cell. G–I, Double-immunofluorescence staining in cells of the hypoglossal nucleus of an SBMA patient revealed diffuse nuclear colocalization of CHIP (G) and mutant AR (H, I). J–L, CHIP (green; J) and mutant AR (red; K) were also colocalized in NIs (shown in yellow; L) in the spinal anterior horn cell of SBMA patients.
