Figure 3.
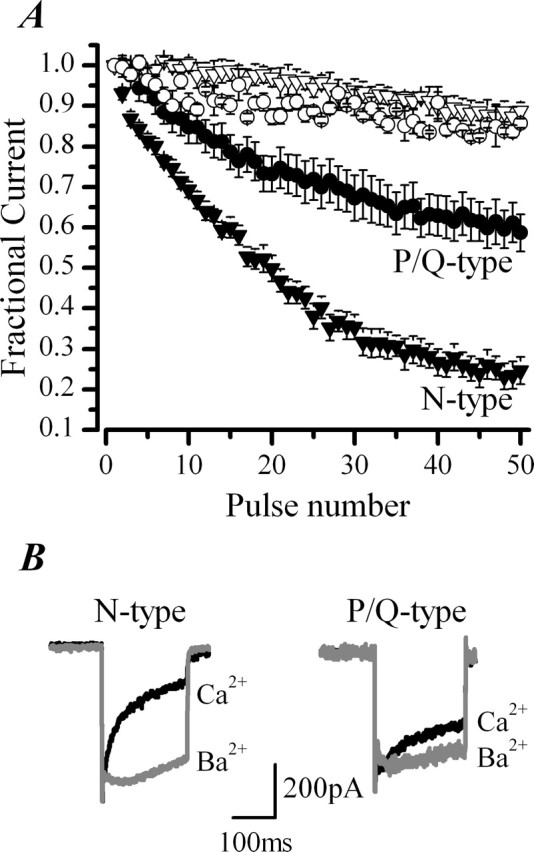
CDI is more pronounced in N-type channels than P/Q-type channels in chromaffin cells. Replacement of extracellular Ca2+ with Ba2+ was used to probe CDI of pharmacologically isolated N- and P/Q-type channels. A, ICa was evoked with a train of 50 pulses of 10 ms duration from −80 to +20 mV, delivered at 20 Hz. Mean ± SEM data are from n = 10 cells recorded in perforated-patch conditions in either the presence of 300 nm AgaIVA to isolate N-type channels (▿, ▾) or 1 μm CgTX to isolate P/Q-type channels (○, •). Cells were stimulated first in control external solution (2.5 mm Ca2+) (▾, •) and then after equimolar replacement with Ba2+ (▿, ○). The difference in CDI between N-type and P/Q-type channels at the 50th pulse in Ca2+ is significantly different (p < 0.0001). B, Superimposed current traces of pharmacologically isolated N-type and P/Q-type channels recorded in response to a 200 ms depolarization from −80 to +20 mV before and after replacement of extracellular Ca2+ (black trace) with Ba2+ (gray trace). I200/Ipeak for N-type channels in Ca2+ was 40 ± 7% (n = 15) compared with 98 ± 1% (n = 3) in Ba2+ and for P/Q-type currents I200/Ipeak increased from 53 ± 6% (n = 15) in Ca2+ to 84 ± 3% (n = 5) in Ba2 +.
