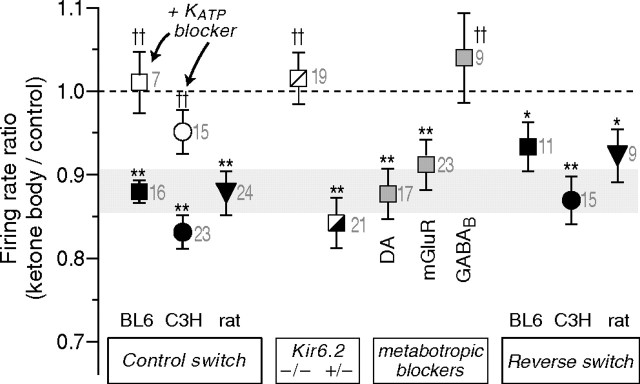
Figure 3.
Ketone body effects on firing rate and their dependence on KATP channels and GABAB receptors. For each condition, the firing rate of many individual cells was monitored for 30–40 min after a metabolic switch, and the firing rate for the final 5 min was normalized to the firing rate before the switch. The metabolic switch was from glucose to glucose plus βHB (2 mm) for all except rat, which was glucose to glucose plus AcAc (2 mm); the final three symbols indicate results for the reverse switch from ketone body containing solution to glucose alone, plotting the initial rate divided by the final rate. The shaded zone indicates the 95% confidence interval for the forward switch in βHB on BL6 cells. The KATP blocker was tolbutamide, present at 200 μm for at least 10 min before the switch (300 μm for C3H slices). The metabotropic blockers (also present for at least 10 min before the switch; BL6, shaded squares) were the dopamine receptor antagonist fluphenazine (1 μm), the mGluR antagonists CPPG (200 μm) and CPCCOEt (100 μm), and the GABAB antagonist CGP55845 (2 μm). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 for difference from 1 by Student's t test; †† p < 0.01 for difference from the corresponding control group, by a Mann–Whitney U test. Numerals next to data points indicate number of experiments.