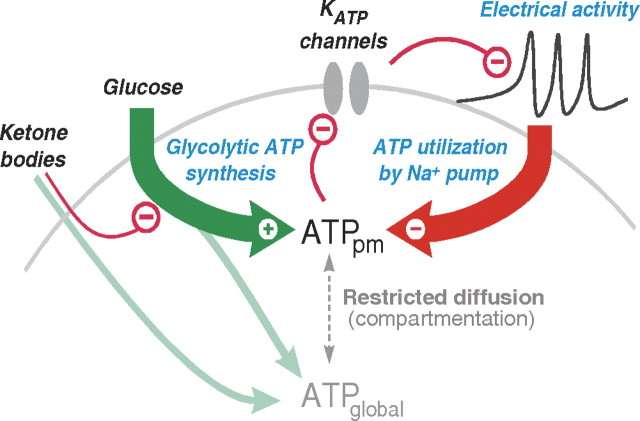
Figure 6.
Hypothesis for the anticonvulsant effect of ketone body metabolism. Metabolism of ketone bodies raises global ATP but reduces glycolysis and glycolytic ATP synthesis. The reduction in [ATP] near the plasma membrane (ATPpm) can disinhibit KATP channels and thus reduce electrical activity. High electrical activity (as in a seizure) increases Na+ influx and thus Na+ pump activity and ATP utilization near the plasma membrane. This produces negative feedback on activity through the KATP channels. The set-point at which this negative feedback safety mechanism becomes active is determined by the level of glycolytic ATP synthesis.