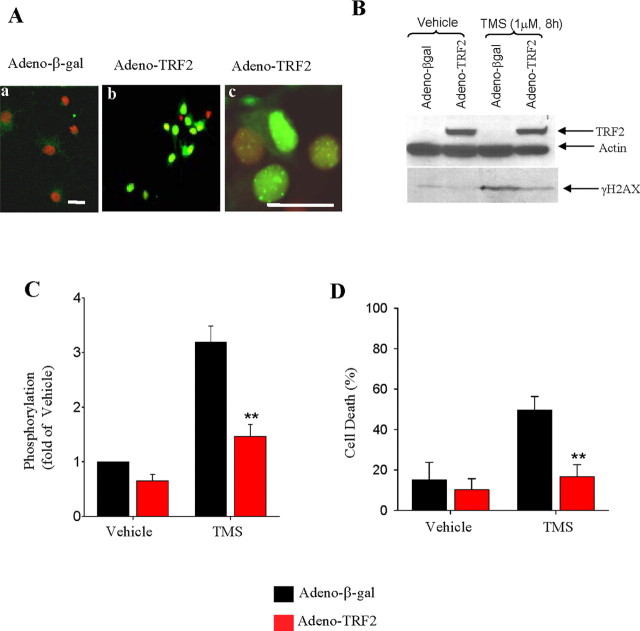
Figure 4.
TRF2 suppresses the DNA damage response and protects NGNs against telomere damage-induced death. A, Confocal images of TRF2 immunostaining of NGNs after 2 d of infection with adeno-βgal or adeno-TRF2. Endogenous TRF2 expression in NGN is very low (Aa), and the virally expressed TRF2 is mainly in the nucleus (Ab) where it is concentrated in foci consistent with a telomeric localization (Ac). The infection efficiency was ∼90%. Scale bars, 20 μm. B, After 2 d of infection with adeno-βgal or adeno-TRF2, NGNs were treated with 1 μm TMS or vehicle for 8 h. Cell lysates were then subjected to immunoblot analysis using antibodies against TRF2, γ-H2AX, and actin. The immunoblot shows that TMS induces an increase in levels of γ-H2AX, and overexpression of TRF2 suppresses this response. C, Densitometric analysis of γ-H2AX levels in NGNs that had been exposed to the indicated treatments. Data are mean ± SD (fold of the vehicle control). **p < 0.001; n = 3. D, Control (adeno-βgal) and TRF2-overexpressing NGNs were exposed to 1 μm telomestatin for 48 h and then stained with Hoechst dye; cell death was quantified by counting cells with condensed nuclei. Data are the means ± SD of three independent experiments. **p < 0.001, paired Student's t test.