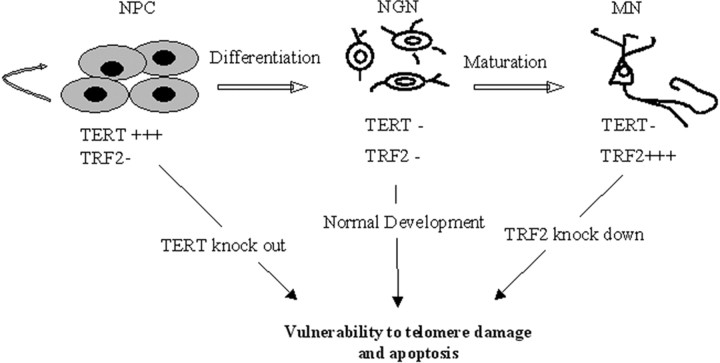
Figure 8.
Model for the roles of TRF2 and TERT in the regulation of neuronal survival and differentiation. NPCs express high levels of TERT but low levels of TRF2. TERT promotes NPC survival. NGNs, which normally have low levels of both TERT and TRF2, are highly sensitive to telomere and DNA damage and apoptosis. MNs, which have low levels of TERT and high levels of TRF2, are relatively resistant to telomere and DNA damage and apoptosis. Depletion of TRF2 from MNs by RNA interference technology (knockdown) renders the MNs vulnerable to telomere and DNA damage and apoptosis. Thus, TRF2, TERT, and telomere state play important roles in determining the vulnerability of NPCs, NGNs, and MNs during brain development.