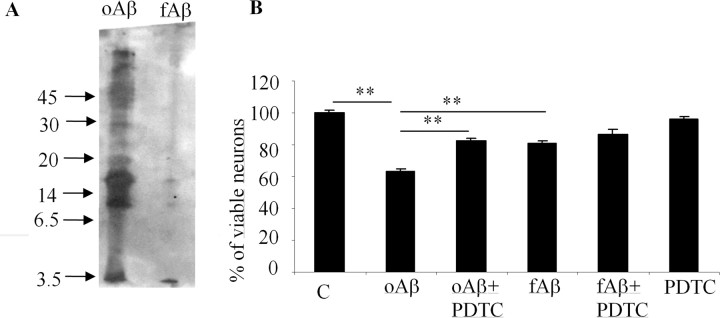
Figure 10.
PDTC protected primary hippocampal neurons against oligomer-rich Aβ induced toxicity. A, Freshly dissolved Aβ preparation contained mostly oligomers, ranging from monomeric Aβ to high-molecular-weight forms. Fibrillization of Aβ resulted predominantly in high-molecular-weight aggregates that did not penetrate into the SDS-PAGE gel used in the current study. B, Exposure of primary hippocampal neurons to the freshly dissolved, oligomer-rich Aβ preparation caused ∼40% cell death as analyzed by the appearance of condensed chromatin. The cell death was significantly diminished by cotreatment with 1 μm PDTC. Fibrillar Aβ was also toxic causing ∼20% cell death, although the effect was significantly smaller compared with oligomer-rich preparation. PDTC failed to protect the neurons against fibrillar Aβ toxicity. PDTC alone did not affect the cell viability. Error bars indicate SEM. *p < 0.01.