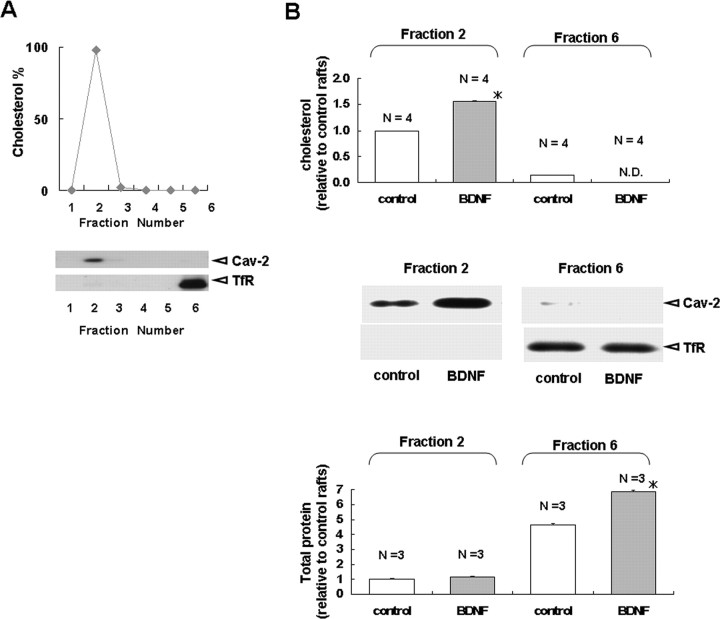
Figure 5.
BDNF increases the amount of cholesterol and caveolin-2 in neuronal lipid rafts. Cortical neurons were cultured in the presence or absence of BDNF (200 ng/ml) for 3 d. A, Lipid raft preparation. Cultured cortical neurons were homogenized in ice-cold lysis buffer containing Triton X-100 and centrifuged in discontinuous 5–35% sucrose gradients. Six fractions (from top to bottom) were collected. Top, The graph shows the cholesterol content in each fraction as a percentage of the total measured cholesterol, revealing peak cholesterol in the raft fraction (fraction 2). Bottom, Six fractions were separated on SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted for the indicated proteins. The lipid raft marker caveolin-2 is enriched in fraction 2, for which cholesterol concentration is the highest, whereas a nonraft marker protein, TfR, is concentrated in fraction 6. B, Effect of BDNF on the amount of cholesterol, total protein, caveolin-2, and TfR. Fractions 2 and 6 were used to represent lipid rafts and nonraft domains, respectively. Top, BDNF significantly increased cellular cholesterol in the raft fraction, but not in the nonraft fraction. Results are presented relative to the control group in fraction 2. Middle, BDNF increased the amount of caveolin-2 in rafts but did not affect the distribution of the TfR. Bottom, BDNF significantly increased the total protein content of the nonraft fraction. Results are presented relative to the control group in fraction 2. The asterisks indicate a statistically significant difference from the control (Student's t test; *p < 0.001).