Figure 8.
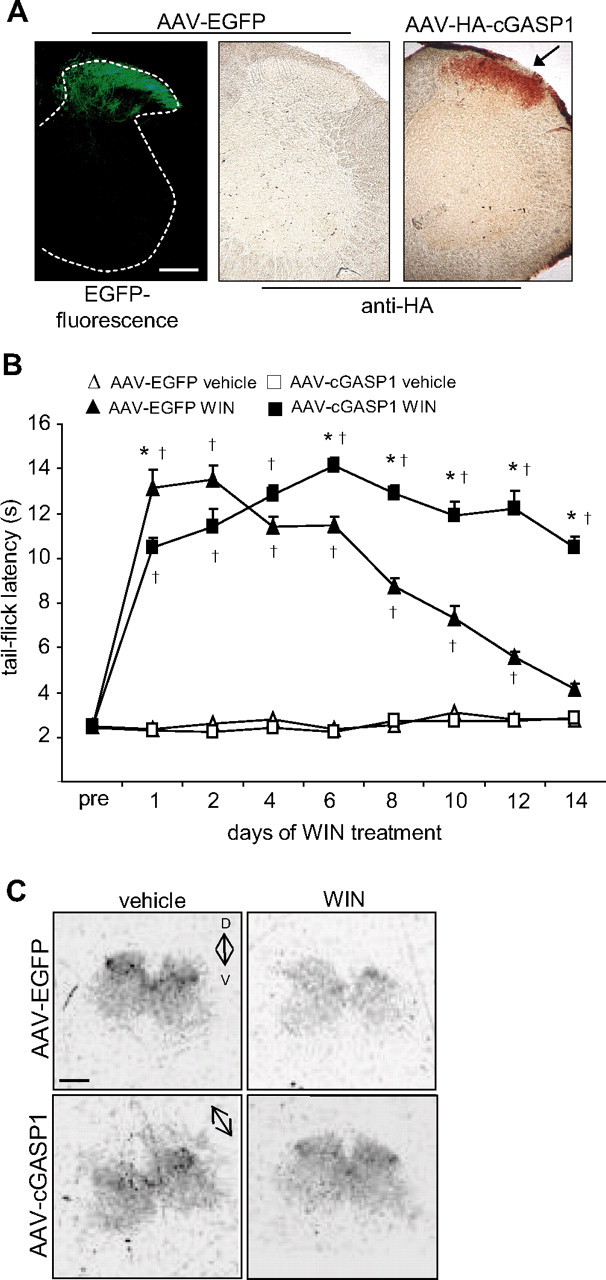
Viral expression of cGASP1 attenuates tolerance and CB1 downregulation in vivo after repetitive treatment with WIN. AAV virions expressing EGFP or HA-tagged cGASP1 were injected into the spinal parenchyma of mice, and experiments were performed 3 weeks later. A, Representative spinal cord sections showing EGFP fluorescence or anti-HA immunoreactivity in the spinal dorsal horn in AAV–EGFP-injected and AAV–HA–cGASP1-injected mice, respectively. B, Mice injected intraspinally with AAV–EGFP demonstrated tolerance to the antinociceptive effects of WIN in the tail-flick test, whereas mice injected intraspinally with AAV–HA–cGASP1 continued to show a WIN-induced increase in tail-flick latency 8–14 d after viral infection. * indicates significant difference compared with AAV-EGFP mice receiving WIN. † indicates significant difference compared with mice receiving vehicle. C, Typical examples of autoradiographic analysis of CB1 expression with the synthetic CB1 agonist 3H-CP-55940 on spinal dorsal horns of spinal cords from mice treated as shown in B. *†p < 0.001, ANOVA, post hoc Fisher's test. n = 8 (AAV–cGASP1 WIN), 6 (AAV–EGFP WIN), 6 (AAV–cGASP1 vehicle), and 4 (AAV–EGFP vehicle) mice. Scale bars: A, 200 μm; C, 100 μm.
