Figure 1.
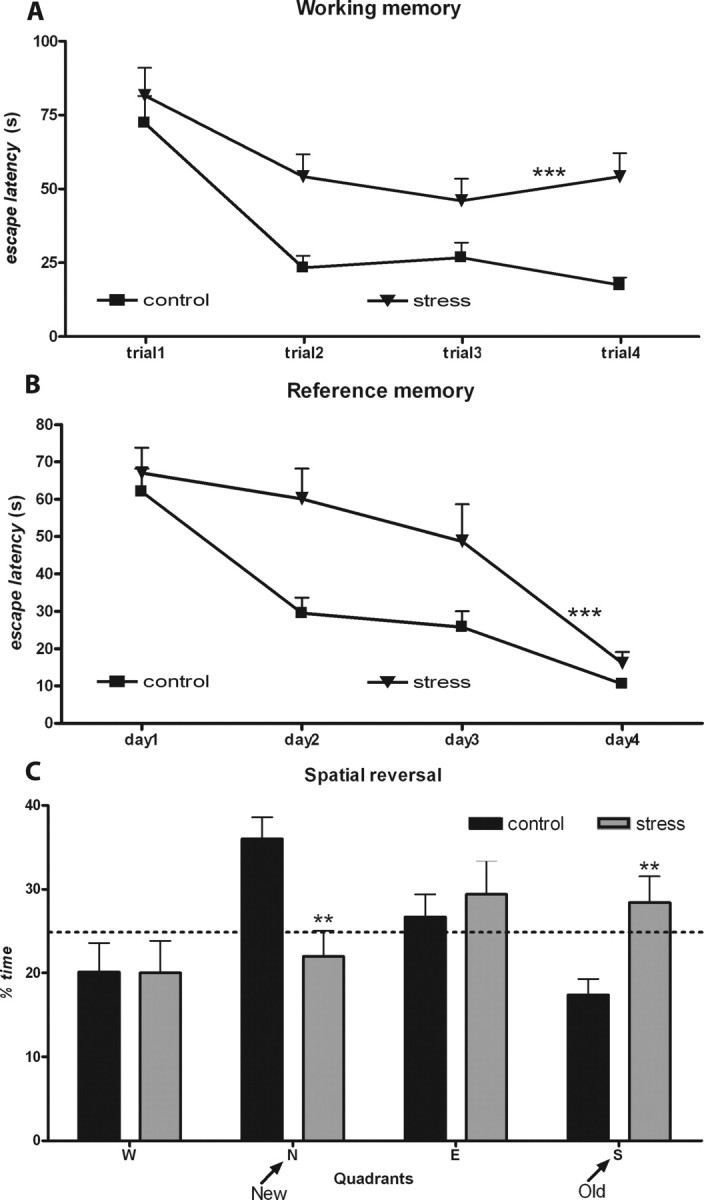
Behavioral impairments induced by chronic stress. A, B, Learning curves in the working (A) and reference memory task (B) of control (n = 10) and chronically stressed (n = 10) rats. The higher escape latencies of the stressed animals are easily appreciated. C, Results from the reverse task experiment. Average time spent on the four trials in each imaginary quadrant is given as a percentage of the total escape latency. Dotted line represents performance at the chance level (25%). Results of distance swam are not presented. **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 compared with controls. Error bars represent SEM.
