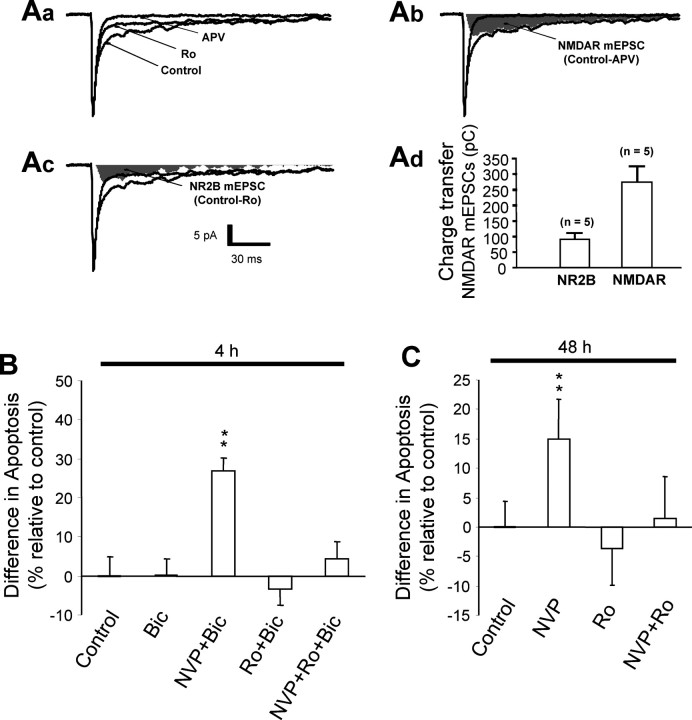
Figure 4.
Activation of synaptic NR1/NR2B NMDA receptors produces a proapoptotic action, which is masked by a predominant synaptic NR2A-containing receptor-mediated cell survival-promoting effect. A, Functional synaptic NR2B-containing receptors are present in cortical neurons in culture. Spontaneous mEPSCs were recorded in whole-cell voltage-clamp mode at a holding membrane potential of −60 mV in the presence of TTX (0.5 μm) and bicuculline (10 μm) with 0 added Mg2+. Aa, Examples of mEPSC traces (averaged from 100 individual events) obtained in the absence (Control) and presence of Ro 25–6981 (Ro; 0.5 μm) or the broad spectrum NMDA receptor antagonist APV (APV; 50 μm). Ab, Total NMDA receptor-mediated component of mEPSCs was obtained by subtracting the averaged mEPSC recorded in the presence of APV from the averaged control mEPSC (Control-APV; shaded area). Ac, The NR1/NR2B receptor component was obtained by subtracting the averaged mEPSC recorded in the presence of Ro 25–6981 (Ro) from the averaged control mEPSC (Control-Ro; shaded area). Ad, Bar graph summarizes data obtained from five individual neurons. Charge transfer is equivalent to the area of the shaded regions. B, Enhanced activation of synaptic NR2A-containing and NR1/NR2B receptors exerts opposing actions on neuronal survival and death. Potentiation of synaptic NMDA receptor activation was achieved by increasing the presynaptic release of glutamate by incubating cultured neurons with bicuculline (Bic; 50 μm) for 4 h in the absence or presence of NR2-containing receptor-specific antagonists. Blockade of NR2A-containing (Bic+NVP), but not NR1/NR2B (Bic+Ro), NMDA receptors increased neuronal apoptosis. The NR2A blockade-induced apoptosis was prevented by an additional blockade of NR1/NR2B receptors (Bic+NVP+Ro). C, Spontaneously activated synaptic NR2A- and NR2B-containing receptors also have opposing roles in promoting neuronal survival and death. Incubation of neurons with NVP-AAM077 (NVP), but not Ro 25–6981 (Ro), for an extended duration (48 h) in the absence of bicuculline stimulation was sufficient to produce an increase in apoptosis. The NVP-AAM077-induced apoptosis was prevented by addition of Ro 25–6981 (NVP+Ro). Thus, both synaptic NR2A-containing and NR1/NR2B subpopulations of NMDA receptors are spontaneously activated by presynaptically released glutamate, exerting counteracting effects on cell survival and death, but synaptic NR2A-containing receptor activation is predominant and required for maintaining normal neuronal survival. **p < 0.01 compared with control; n = 16 (B) and 10–12 (C) for each group from three separate experiments.