Figure 8.
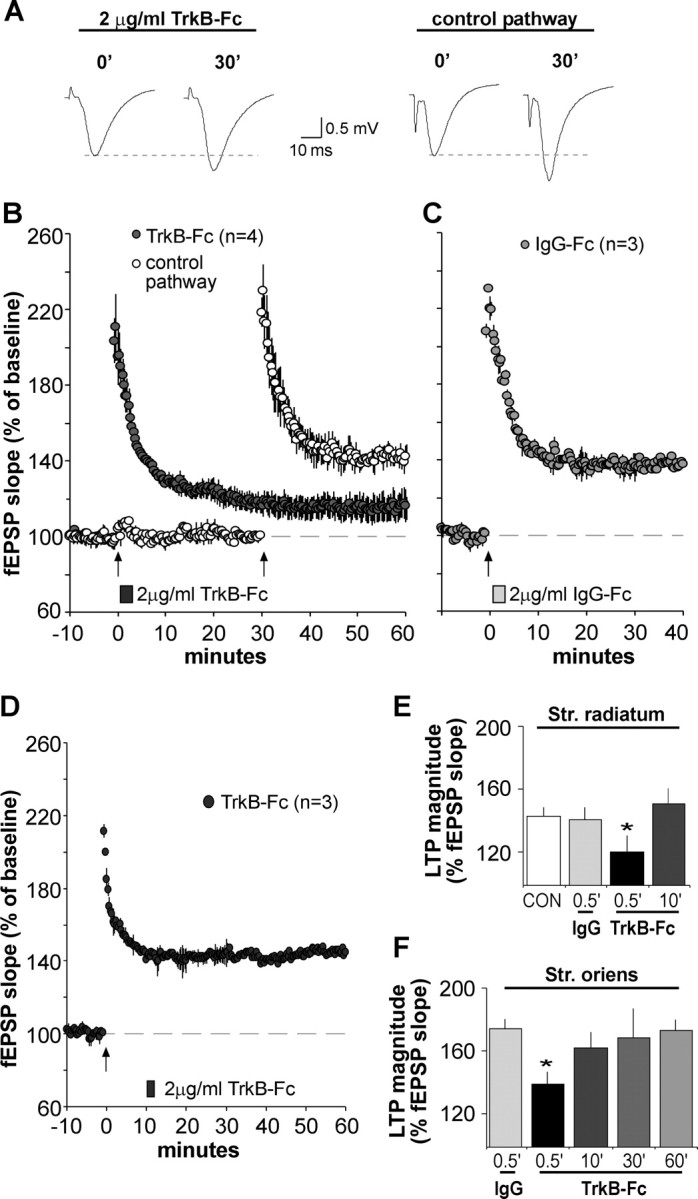
BDNF scavenger TrkB–Fc applied after theta burst stimulation disrupts LTP consolidation. A, Representative fEPSP traces show that the degree of synaptic potentiation produced by a conventional theta burst train was attenuated when TrkB–Fc (2 μg/ml) was applied for 2 min beginning 30 s after TBS. Traces at right (2 μg/ml TrkB–Fc) were collected during baseline (0′) and 30 min after TBS (30′). The experiment was repeated using a second population of synapses (control pathway; traces at left) after the scavenger had been washed out for 27 min. In this case, normal TBS-induced potentiation (30min after TBS) was obtained. B, Plot shows group fEPSP slopes (means ± SEM) for experiments described above. Note that potentiation for the pathway receiving post-TBS TrkB–Fc treatment (filled circles), although initially robust, decayed significantly compared with potentiation in the control pathway (open circles); arrow here and in later panels indicates placement of TBS. C, Same as in B except that the control IgG–Fc (2 μg/ml) was infused 30 s after TBS; this had no effect on LTP. D, TrkB–Fc infused for 2 min starting 10 min after TBS had no effect on LTP. E, F, Summary of the percentage of LTP obtained with post-induction infusion of TrkB–Fc or IgG–Fc: values are percentage change from baseline measured 30 min after infusion onset; tests performed in apical (str. radiatum) and basal (str. oriens) dendrites are summarized in E and F, respectively. For both lamina, TrkB–Fc attenuated LTP expression when applied 30 s after TBS compared with potentiation attained in IgG–Fc-treated controls (*p < 0.05, two-way repeated-measures ANOVA followed by Tukey's HSD) but failed to alter potentiation at later time points.
