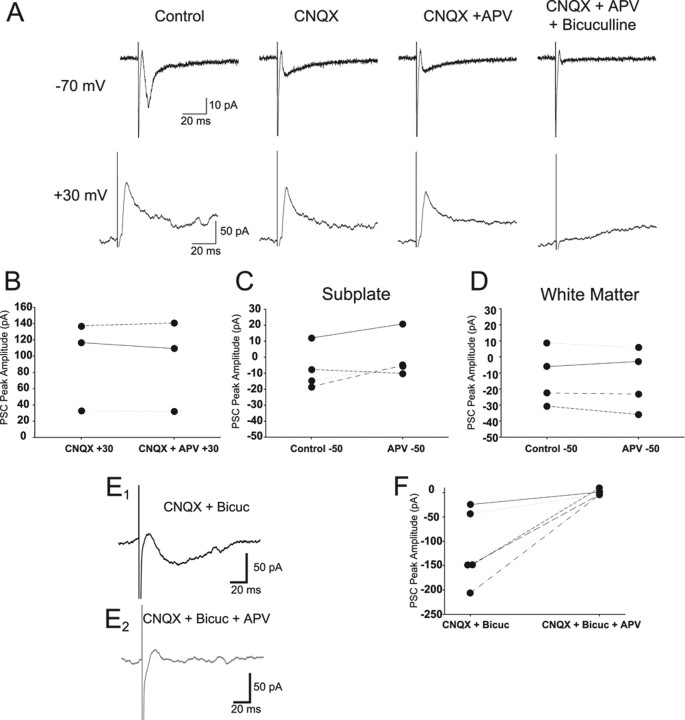
Figure 5.
Effects of APV application on evoked synaptic responses in the presence of CNQX at −70 and +30 mV before and after application of bicuculline. Example (A) synaptic responses of an SP cell recorded at −70 and +30 mV holding potential. An inward (control, −70 mV) and the corresponding outward (+30 mV) current are seen at the two holding potentials. The current is significantly decreased by CNQX at −70 mV (−52%; p < 0.01) but is not significantly affected by APV (−3%; p > 0.05) at either potential. Bicuculline eliminated the remaining current at both membrane potentials. Individual (B) data for SP cells (n = 3) that were depolarized to +30 mV in the presence of CNQX (CNQX + 30) and in the presence of CNQX/APV (CNQX + APV + 30). The NMDA receptor component was not observed when SP (n = 4) (C) or WM (n = 4) (D) cells were depolarized to −50 mV. Inward PSCs are seen at +30 mV when SP cells are recorded in low Mg2+/high Ca2+ and during blockade of AMPA/kainate and GABAA receptors (E1). The current is eliminated by application of APV (E2). Individual data (F) for SP cells (n = 5) depolarized to +30 mV in the presence of CNQX and bicuculline (CNQX + Bicuc) and in the presence of CNQX, bicuculline, and APV (CNQX + Bicuc + APV).