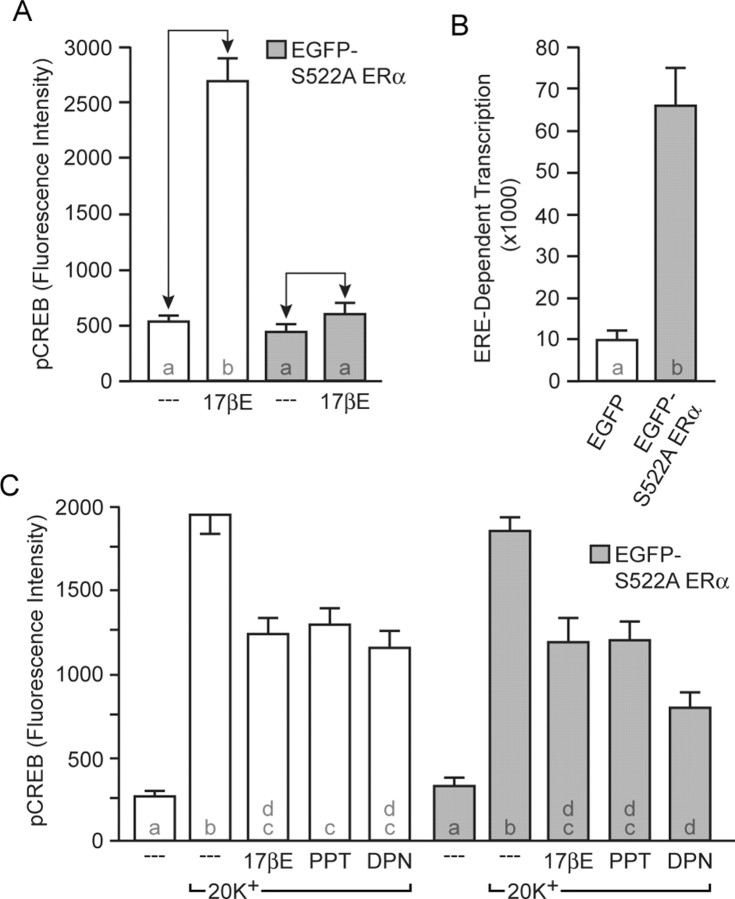
Figure 2.
A single amino acid substitution in ERα disrupts estradiol-dependent CREB phosphorylation without affecting two other actions of estradiol. A, Transfection of cultured hippocampal neurons with EGFP-S522A ERα, a construct that inhibits CAV1-mediated ERα membrane trafficking in non-neuronal cells, blocked estradiol-induced CREB phosphorylation (F = 61.66). B, EGFP-S522A ERα activates ERE-dependent transcription (t = 5.87). C, EGFP-S522A ERα did not effect estradiol-mediated attenuation of L-type calcium channel-dependent CREB phosphorylation (F = 31.88). Both the ERα (PPT, 1 nm) and ERβ (DPN, 10 nm) agonists were effective in the presence of EGFP-S522A ERα to attenuate depolarization-induced CREB phosphorylation. In this and all subsequent figures, alphabetical characters within each bar indicate statistical differences between groups (p < 0.05), and differences in the effect of estradiol before and after experimental treatment are indicated by the arrowed brackets. Error bars depict SEM. 17βE, 17β-Estradiol.