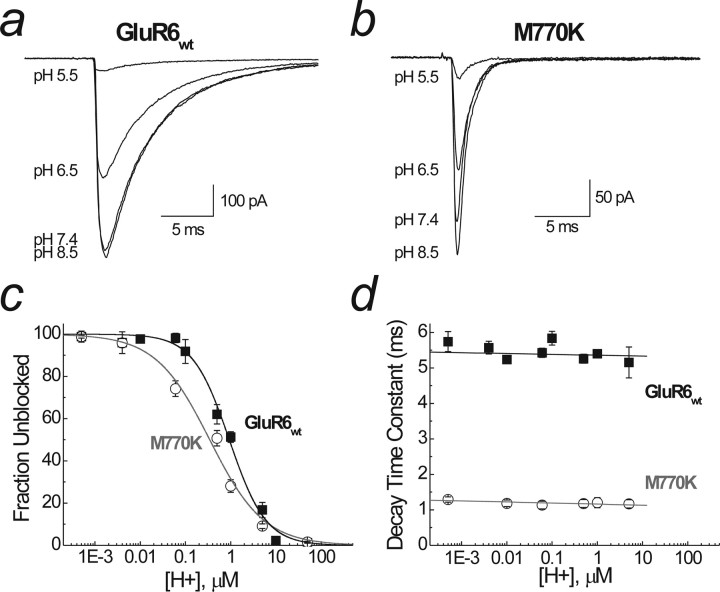
Figure 3.
pH modulation of GluR6wt and GluR6M770K. a, Raw data showing the effect of lowering pH (i.e., increasing H+ concentration) on wild-type GluR6 receptors (patch 04615p3). b, The effect of lowering pH on GluR6M770K (patch 06525p1). External acidification leads to a decrease in amplitude but no change in the decay kinetics of both GluR6wt and GluR6M770K. c, Pooled data for an extended pH range for GluR6wt (black squares) and GluR6M770K (white circles). Dose–response curves were best fitted with a single binding site isotherm, with Imax constrained to 100%. The IC50 was pH 6 for GluR6wt, and pH 6.8 was for GluR6M770K. Hill slopes (nH) were 1 and 0.7, respectively. d, The effect of pH on channel decay kinetics. Data were fitted with a linear fit, and there was no significant change in decay kinetics with decreasing pH in both wild-type (black squares) and mutant (white circles) receptors. Data are mean ± SEM of at least six patches for each pH.