Figure 4.
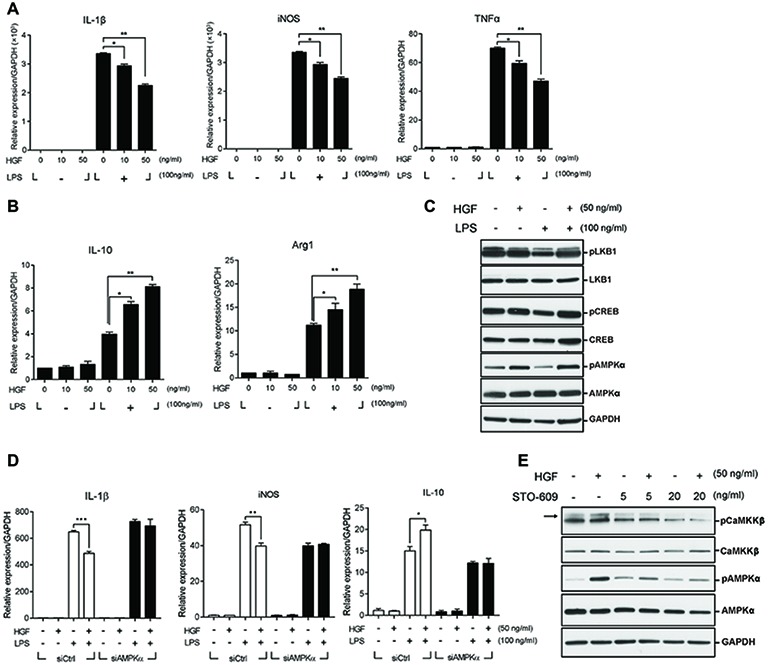
Roles of CaMKKβ-AMPKα on HGF-mediated control of the expression of M1 and M2 markers in Raw 264.7 cells. Raw 264.7 cells were cultured in the presence or absence of LPS and recombinant HGF proteins. Total RNA and proteins were prepared and analyzed by RT-qPCR and western blot, respectively. (A) Effects of HGF on the RNA levels of M1 markers (IL-1β, iNOS, and TNFα). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 (unpaired student’s t test), n = 3 per group. (B) Effects of HGF on RNA levels of M2 markers (IL-10 and Arg1). Values were normalized to GAPDH. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 (unpaired student’s t test), n = 3 per group. (C) Effects of HGF on signaling pathways related to macrophage polarization. (D) Effects of AMPKα knockdown on HGF-mediated regulation of the RNA level of IL-1β, iNOS, and IL-10, marker genes of M1 and M2. Raw 264.7 cells were transfected with AMPKα or control siRNAs, and then treated with LPS and HGF. Values were normalized to GAPDH. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 (unpaired student’s t test), n = 3 per group. (E) Effects of CaMKKβ inhibitor, STO-609, on the HGF-mediated phosphorylation of AMPKα. Arrow indicates the protein of interest in blots. In western blot hybridization, GAPDH was used as a loading control. All data are presented as mean ± SEM. See also Supplementary Figure S2 and S3.
