Figure 7.
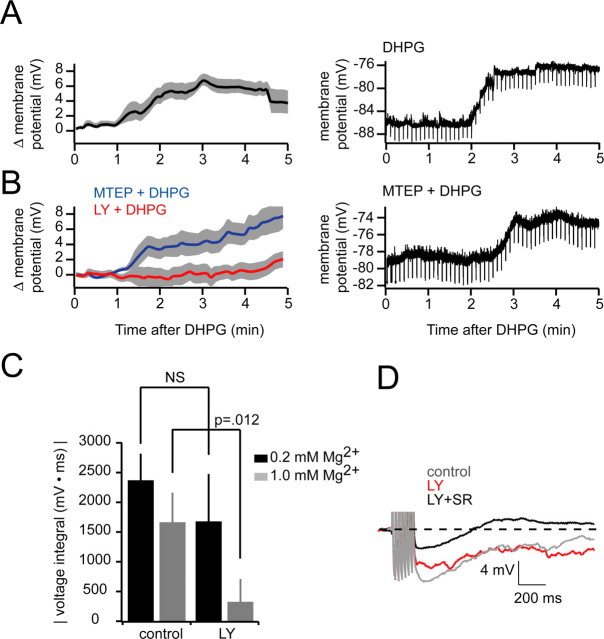
DHPG depolarizes granule cells. A, Left, Group data showing granule cell depolarization with addition of DHPG (20 μm) starting at t = 0 (n = 4; mean depolarization, 6.79 ± 0.79; shaded areas indicate ±SEM). Right, An example experiment is shown. Negative-going deflections are hyperpolarizing pulses used to monitor input resistance. B, Same layout and experimental design as in A, only with 2 μm MTEP (n = 5) or 100 μm LY (n = 5) included in the bath to block mGluR5 or mGluR1, respectively. Right, Example experiment showing persistence of DHPG-evoked granule cell depolarization when mGluR5 is antagonized. C, Effectiveness of LY in blocking RI at normal (1.0 mm; n = 7) and low (0.2 mm; n = 6) magnesium concentrations. D, Single sample sweeps showing RI after seven evoked spikes at 40 Hz in 0.2 mm Mg2+. Gray, Control; red, after LY alone; black, LY plus gabazine.