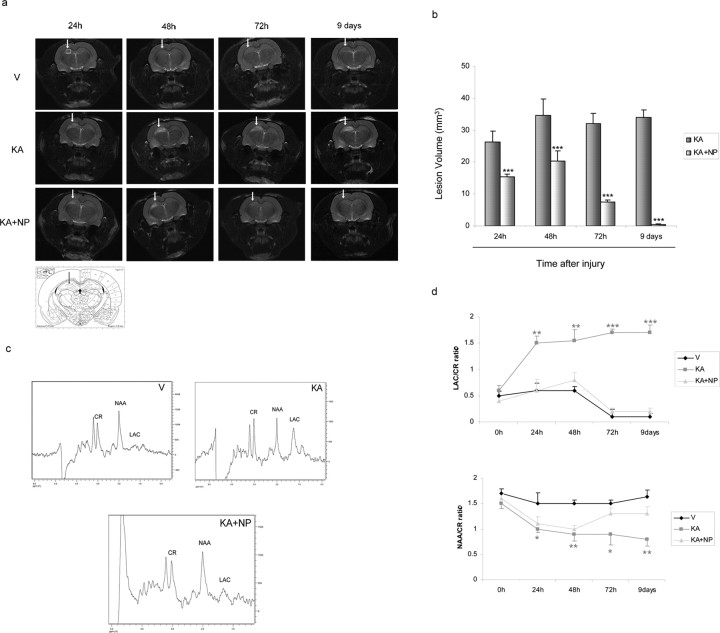
Figure 2.
Effect of NP031112 on KA-induced brain edema as detected by MRI. T2-weighted imaging was performed at 7 tesla as described in Materials and Methods at different times after KA injection. a, Representative coronal images of rat brain injected with vehicle (top), KA (middle), and KA plus NP031112 (bottom). Hyperintensity areas in T2-weighted MRIs reveal regions of edema after KA injection. Hyperintense areas were reduced in the NP031112-treated rats compared with the KA-injected rats, demonstrating a decrease in the injured area. No hyperintensity was found in the vehicle-injected rats. Arrows indicate the injection site. An anatomic diagram (Paxinos, 1998) showing (arrow) the precise localization of the microinjection in the rat hippocampus is shown. b, Quantitative analysis of total lesion volumes of KA- and KA plus NP031112-injected rats. The volume of the edemas was significantly lower in NP031112-treated rats, compared with KA-treated group at all of the times studied. Values represent the mean ± SD from five different animals and five independent sections per animal. ***p ≤ 0.001. c, Representative point-resolved spatially spectra acquired from the hippocampal region (white box) with resonances from NAA, lactate (Lac), and creatine (Cr) 9 d after treatment. d, Time course of variation of NAA or lactate values (mean ± SD) in the ipsilateral hemisphere of control-, KA-, and KA plus NP031112-treated animals during 9 d, normalized to the creatine peak. V, Vehicle; NP, NP031112. *p ≤ 0.05; **p ≤ 0.01; ***p ≤ 0.001, versus vehicle-injected animals at each time point.