Figure 5.
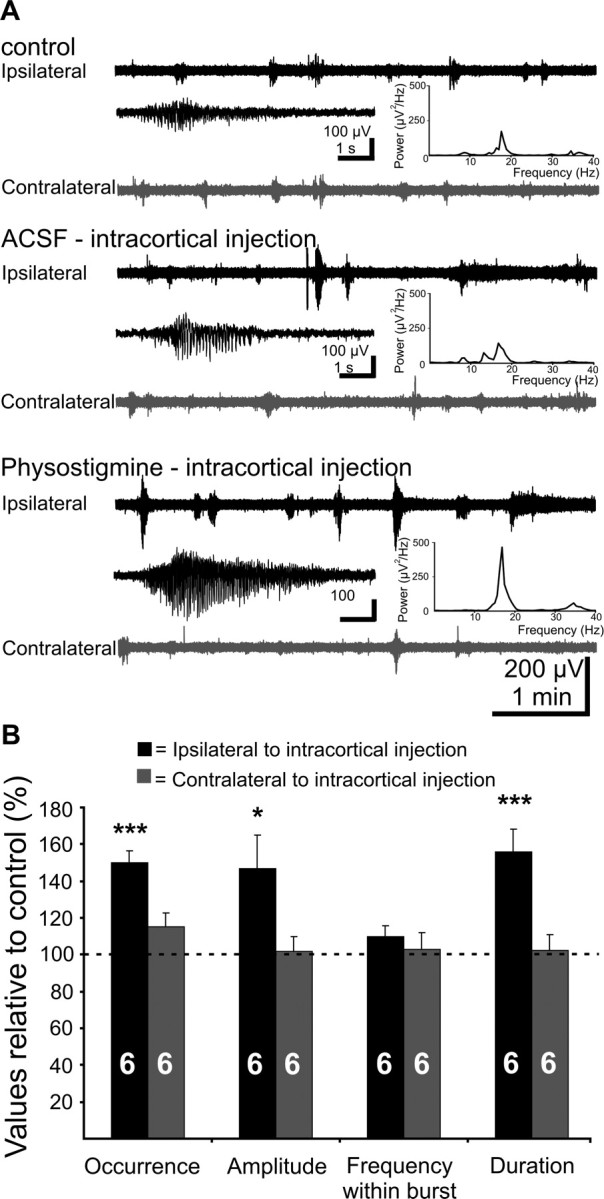
Effects of increased cortical ACh levels by blockade of the AChE with physostigmine on the V1 spindle burst activity of the newborn rat in vivo. A, Extracellular field potential recordings from ipsilateral (black trace) and contralateral (gray trace) V1 of a P6 rat under control conditions, after intracortical injection of 20 nl of ACSF, and after intracortical injection of 20 nl of physostigmine (130 μg/kg body weight, in ACSF). Note the increased occurrence, amplitude, and duration of the V1 bursts on the side of injection. Inset, Typical spindle bursts displayed at an expanded time scale and averaged power spectrum of the field potential oscillations corresponding to the displayed traces. Note the dramatic physostigmine-induced increase in the burst power. B, Bar diagram displaying the effects of physostigmine on the occurrence, amplitude, frequency within burst, and duration of ipsilateral (black bars) and contralateral (gray bars) V1 bursts of six pups. Control values recorded before physostigmine application were considered as 100%. The hemisphere of intracortical injection was defined as ipsilateral.
