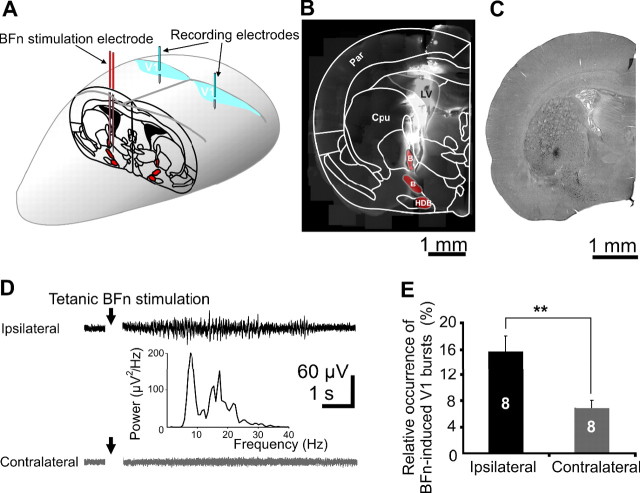
Figure 6.
Modulation of the V1 spindle bursts by electrical stimulation of the BFn. A, Schematic drawing of the BFn-stimulation (red) and V1 recording (blue) paradigm. B, Digital photomontage of DiI-labeled stimulation electrode in a 400-μm-thick coronal brain section superimposed on a schematic drawing of a coronal section of P0 rat brain. The basal forebrain nuclei with a high density of cholinergic neurons projecting to the V1 are marked in red. B, Nucleus basalis; Cpu, caudate putamen; HDB, horizontal limb diagonal band, LV, lateral ventricle; Par, parietal cortex (following Paxinos et al., 1991). C, Photograph of a coronal section (50 μm thick) from a P6 rat after immunostaining for VAChT. Note the presence of cholinergic neurons (black dots) in different nuclei of the basal forebrain. D, Extracellular recordings of the ipsilateral (black trace) and contralateral (gray trace) cortical response to electrical tetanic stimulation of the BFn in a P6 rat. Note the spindle bursts elicited on the ipsilateral side to stimulation and the absence of such response on the contralateral side. The displayed traces correspond to 20 averaged responses to BFn stimulation. E, Power spectrum of the averaged BFn-induced V1 bursts from the trace shown in D. The side of stimulation was defined as ipsilateral.