Figure 1.
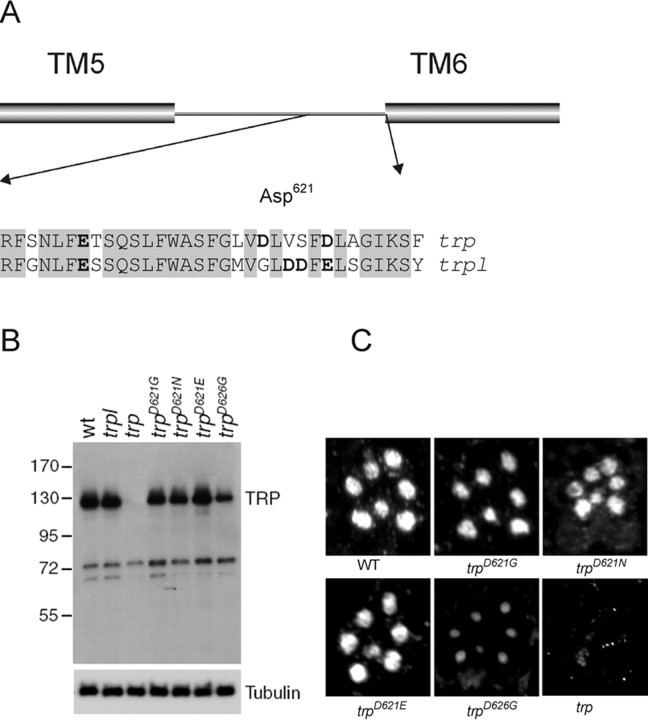
Generation and expression of mutations in acidic residues in putative selectivity filter. A, Alignment of TRP and TRPL sequences in the vicinity of the putative pore region, which by analogy to other channels would be expected to be located toward the end of the region linking TM5 and TM6. Acidic residues are indicated in bold. A total of 78% of residues are identical in this region (shaded). Asp621 and Asp626 are the only acidic residues unique to TRP sequence. B, Western blot showing TRP protein levels in trpl, wild-type, trp, and the four transgenic lines used in this study: trpD621G, trpD621N, trpD621E, and trpD626G. The blot was also probed with α-β-tubulin antibodies to provide a loading control. C, Immunofluorescent localization of mutant TRP isoforms in semithin LR White sections stained with α-TRP antibodies. Each image shows the pattern of rhabdomeres in one ommatidium. All TRP isoforms were correctly localized, although the TRPD626G signal was weaker because of the lower level of expression. No staining above background was seen in the negative control (trp), which was the null allele trp343 (Wang et al., 2005).