Figure 6.
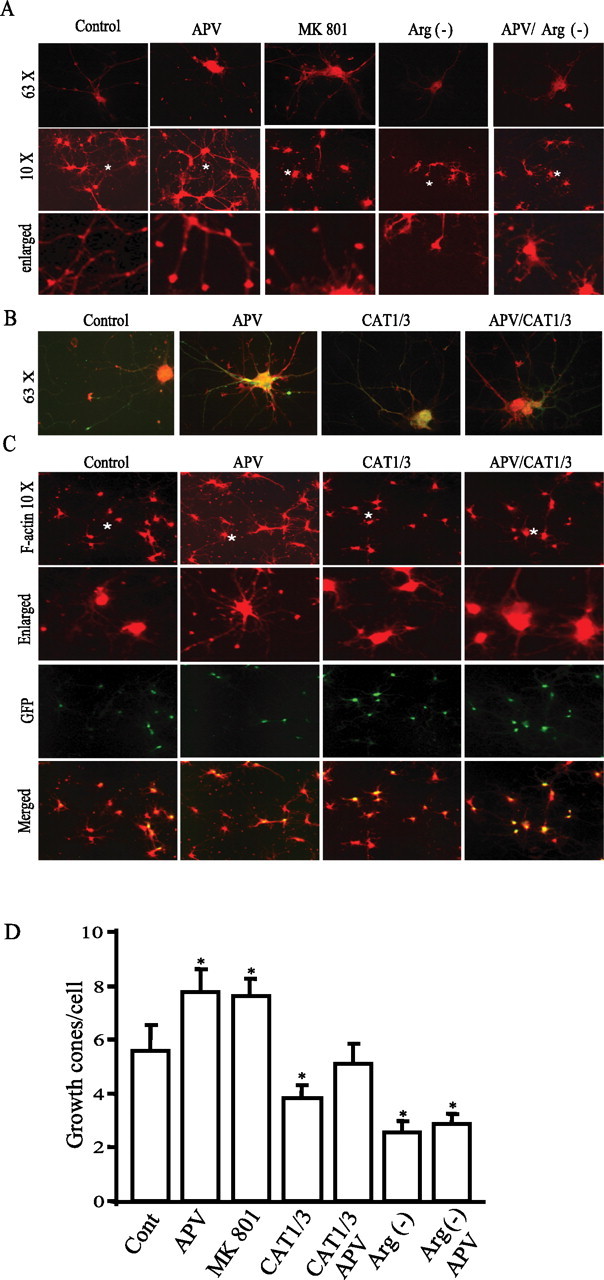
Arginine bioavailability regulates growth cone formation. A, F-actin staining and growth cone formation. Cortical neurons at in vitro day 4 were treated with 50 μm APV or 20 μm MK801 in Neurobasal medium with or without arginine/lysine. F-actin was stained with phalloidin conjugated with TRITC. Images in the top and middle rows were taken at high power (with 63× lens) and low power (with 10× lens), respectively. The F-actin puncta (fine dots) in images reflect growth cones. The images in the bottom row are derived from regions marked with a symbol * in the images in the middle row. B, C, Neurons at approximately in vitro day 3–4 were infected with RNAi lentivirus and then treated with 50 μm APV at 2 d after infection. Neurons at in vitro day 10 were stained with phalloidin conjugated with TRITC (63× in B and 10× in C). Colocalization reveals that almost all neurons stained with F-actin are GFP positive, indicating that they are infected with RNAi lentivirus. D, Quantification of growth cones. Data for each group is averaged from 70–100 cells from 10 images acquired at low magnitude (10×) (in growth cones/cell: control, 5.58 ± 0.98; APV, 7.78 ± 0.84; MK801, 7.59 ± 0.67; CAT1/3, 3.81 ± 0.49; CAT1/3 plus APV, 5.12 ± 0.75; arginine-minus [Arg(−)] condition, 2.56 ± 0.42; arginine-minus condition plus APV, 2.87 ± 0.36). *p < 0.05.
