Figure 2.
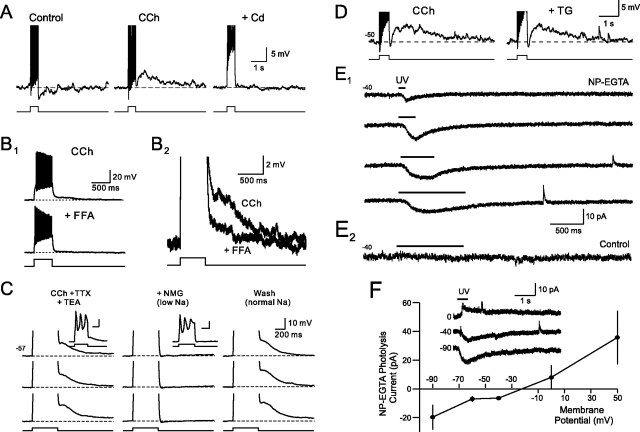
Mechanism of afterdepolarization in granule cells. A1, Cadmium (Cd; 200 μm) abolishes the afterdepolarization evoked in granule cells by 25 pA depolarizing steps in 2 μm CCh. A2, Summary of the effect of Cd on ADP amplitude. *p < 0.01. B1, Flufenamic acid (100 μm) blocks the ADP in CCh. B2, Enlargement of CCh and CCh + FFA responses. Action potentials truncated in A1 and B2. C, ADPs evoked by Ca spikes in 2 μm CCh, 1 μm TTX, 25 mm TEA, 100 μm 4-AP and 4 mm CsCl. Reducing the Na driving force by applying an ACSF solution containing 99 mm NMG reversibly blocked the ADP (“+NMG”). Responses to 90 pA steps are truncated to illustrate afterpotentials. Example responses in CCh and CCh + NMG conditions shown in the insets. D, Thapsigarin (TG; 10 μm) did not reduce the ADP response in granule cells exposed to 2 μm CCh (50 pA step). E1, Photolyzing NP-EGTA (2 mm; added to the internal solution) evokes a graded inward current in voltage-clamped granule cells. Horizontal lines above each trace indicate UV exposure time (100, 250, 500, and 1000 ms). E2, UV exposure by itself does not evoke an inward current in control granule cells that were not loaded with NP-EGTA. F, Uncaging response reversed polarity at approximately −20 mV (data from 5 experiments). The inset shows example responses recorded at 0, −40, and −80 mV.