Figure 4.
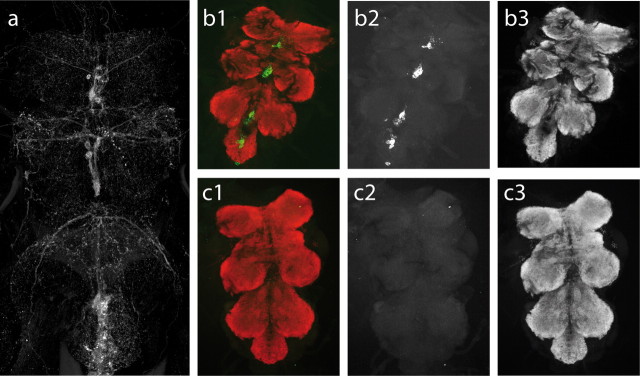
Genetic ablation of all tyraminergic and octopaminergic neurons. a, Visualization of all tyraminergic and octopaminergic neurons in the thoracic and abdominal ventral nerve cord by expressing 2xeGFP under the control of Tdc2 and enhancing the signal by anti-GFP immunocytochemistry. To test the effectiveness of neuron ablation by targeted ectopic expression of the cell death gene reaper, animals expressing either only GFP or GFP together with reaper were subjected to standard immunohistochemistry. Animals expressing only GFP reveal the expression pattern typical of Tdc2 neurons. b1 shows double labels of the ventral nerve cord for Tdc2 neurons labeled by targeted expression of eGFP (green) and all synapses labeled with bruchpilot antibody Nc82 (Kittel et al., 2006) (red) to visualize presynaptic active zones in the neuropil regions. b2 and b3 show the Tdc2 and the Nc82 signal separately as grayscale images. b1–b3 show a ventral nerve cord from heterozygous progeny of dTdc2–Gal4 crossed with y w P{w+mC=UAS–2xEGFP}. c, Gal4-driven apoptosis was induced by crossing dTdc2–Gal4 with w;; P{UAS-rpr}/TM3 Sb, and eGFP was from y w P{w+mC=UAS–2xEGFP}. No GFP expression can be detected in animals with targeted expression of both GFP and reaper to these OA/TA cells (c1), but Nc82 immunostaining appears unaffected in these animals (c3), demonstrating effective and specific ablation.