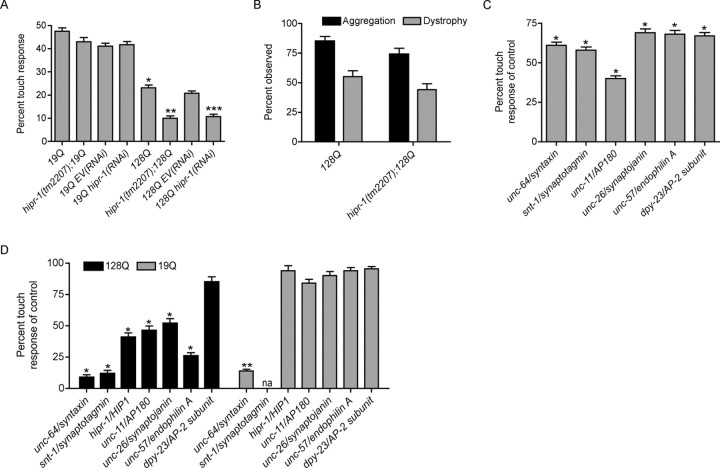
Figure 6.
hipr-1 protects against mutant polyQ neuronal dysfunction. A, Mutation or RNAi of hipr-1 decreased touch responsiveness in animals expressing mutant htt. *p < 0.001 compared with 19Q alone; **p < 0.001 versus 128Q alone; ***p < 0.001 versus 128Q RNAi controls (n = 200 for all experiments). B, In vivo analysis revealed no change in the frequency of either the aggregation of huntingtin fusion proteins or dystrophy along axonal processes (n = 200). C, Synaptic genes are required for wild-type touch response. The percentage of wild-type response is given for each LOF synaptic mutant. *p < 0.001 compared with wild type (n = 200). D, Synaptic genes associated with endocytosis protect against mutant polyQ neuronal dysfunction. The percentages of either 128Q or 19Q touch response for each LOF mutant are given. *p < 0.001 versus 128Q animals; **p < 0.001 compared with 19Q controls (n = 200 for all experiments).