Figure 1.
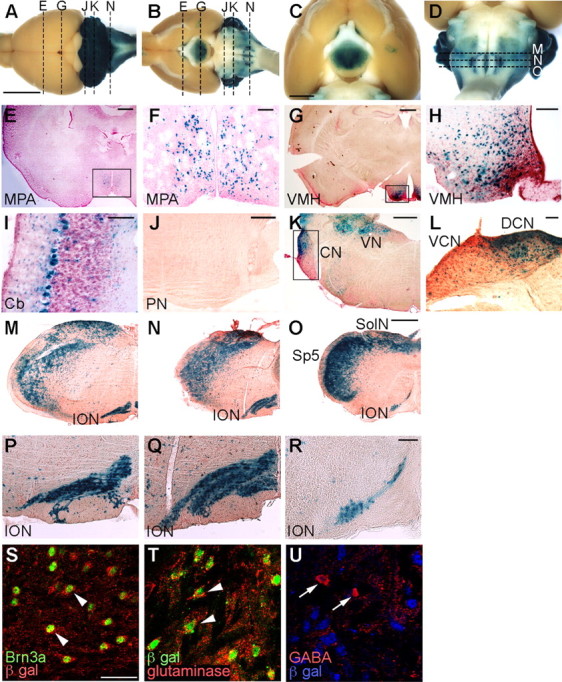
Cells in the Ptf1a lineage were visualized by X-gal staining of Ptf1acre/+; R26R adult brains. A–D, Dorsal (A) and ventral (B–D) views of whole-mount X-gal-stained brains. E–L, Transverse sections of X-gal-stained brains at the level of the medial preoptic area (E, F), ventral medial hypothalamus (G, H), cerebellum (I), pontine nuclei (J), and cochlear nuclei (K, L), which correspond to broken lines in A and B. F, H, L, Higher-magnification views of the rectangular regions indicated in E, G, K, respectively. M–O, X-gal-stained transverse sections of adult medulla oblongata of Ptf1acre/+; R26R at the levels of the rostral (M), middle (N), and caudal (O) ION, which correspond to the broken lines in D, respectively. P–R, Higher-magnification views of M–O, respectively. E–R, Transverse sections were counterstained with nuclear fast red or neutral red. S–U, Double immunolabeling visualized with indicated antibodies to the adult ION of Ptf1acre/+; R26R mice. Scale bars: A–D, 5 mm; E, G, J, K, M–O, 500 μm; F, H, I, L, P–R, 100 μm; S–U, 40 μm. MPA, Medial preoptic area; VMH, ventral medial hypothalamic nucleus; Cb, cerebellar cortex; PN, pontine nuclei, CN, cochlear nuclei; DCN, dorsal cochlear nucleus; VCN, ventral cochlear nucleus; VN, vestibular nuclei; SolN, solitary nucleus; Sp5, spinal trigeminal nucleus.
