Figure 2.
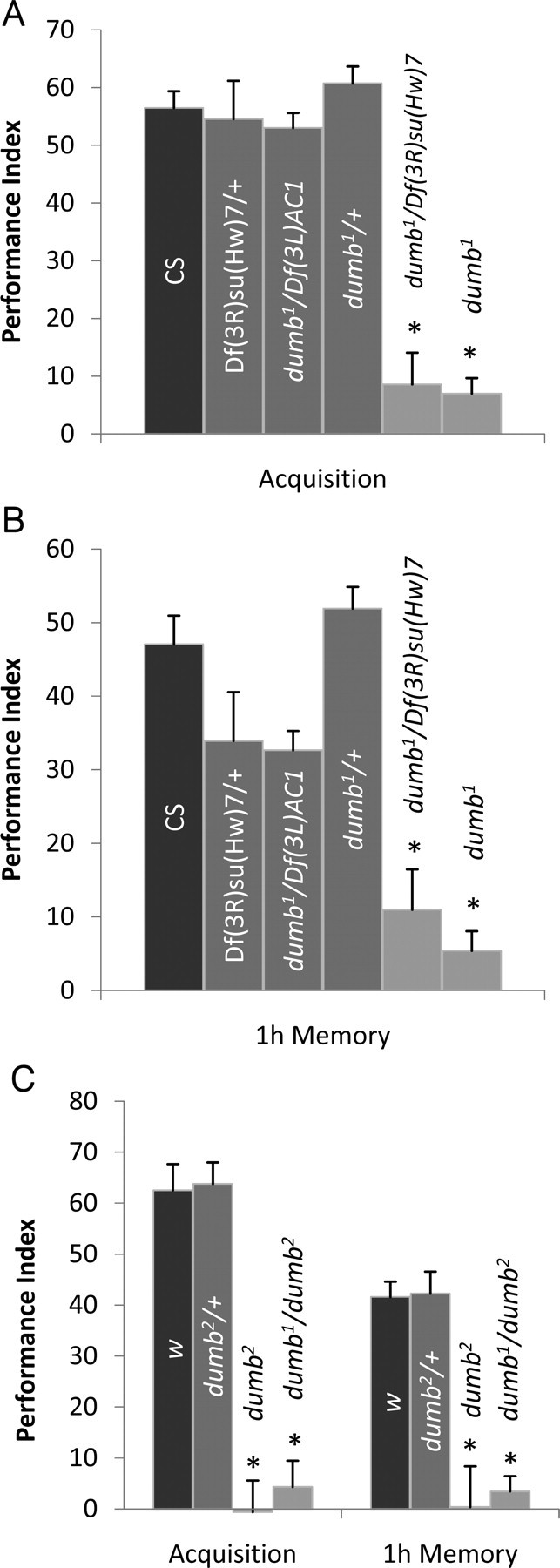
The learning phenotype of dumb mutants in aversive olfactory conditioning. A, B, Flies were trained with BA and OCT as CS and tested immediately after (acquisition) or 1 h after training (1 h memory). A, dumb1 homozygous and dumb1/Df(3R)su(Hw)7 trans-heterozygous mutants exhibited severely impaired learning, whereas dumb1/+, Df(3R)su(Hw)7/+, and dumb1/Df(3L)AC1, which have one copy of the dDA1 gene, showed performance similar to that of Canton-S (AVOVA; F(5,35) = 35.9; p < 0.0001; n = 6 for all groups; asterisks indicate significant difference by post hoc Tukey–Kramer tests). B, At 1 h after training, dumb1, dumb1/Df(3R)su(Hw)7, Df(3R)su(Hw)7/+, and dumb1/Df(3L)AC1 showed defective performance compared with Canton-S and dumb1/+ (ANOVA; F(5,35) = 26.04; p < 0.0001; n = 6; asterisks indicate significant difference compared with Canton-S by post hoc Student's t test). C, dumb2 homozygous and dumb1/dumb2 transheterozygous mutants showed no trace of learning and 1 h memory, whereas learning or 1 h memory performance of dumb2 heterozygous flies (dumb2/+) was similar to that of the genetic control line w1118 (w) (acquisition ANOVA: F(3,23) = 55.3, p < 0.0001; 1 h memory ANOVA: F(3,23) = 21.6, p < 0.0001; n = 6; asterisks indicate significant difference by Tukey–Kramer tests). Error bars indicate SEM.
