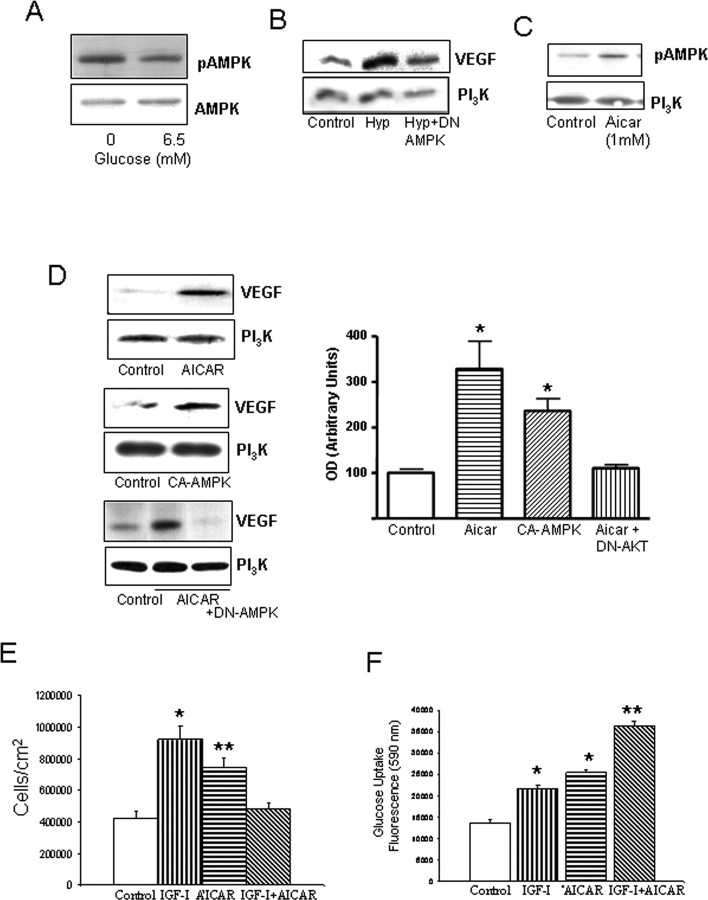
Figure 3.
Actions of AMPK and IGF-I on brain endothelial cells. A, Hypoglycemia increases levels of pAMPK (the active form of the kinase). Brain endothelial cells were kept under 0 or 6.5 mm glucose (euglycemia) for 24 h. Total levels of AMPK were not affected by treatments. B, DN AMPK abrogates stimulation of VEGF in endothelial cells after hypoxia (Hyp). Cells were transfected and, after 2 d, submitted to 24 h of hypoxia. VEGF levels were determined 1 d later. Cells were lysed and immunoblotted with anti-VEGF, and protein load was determined with anti-PI3K. C, Addition of AICAR (1 mm) to the cultures increases pAMPK levels, whereas levels of PI3K remained unchanged. D, Left, Stimulation of AMPK increases levels of VEGF in brain endothelial cells. Cells were treated with AICAR (top blots) or transfected with a CA AMPK (middle blots) or a DN AMPK (bottom blots) for 2 d. Twenty-four hours later, the cells were lysed and immunoblotted with anti-VEGF. Right, In the histograms, densitometric quantification of VEGF levels after AICAR or CA AMPK showed significant increases over baseline (*p < 0.005; n = 4). Representative blots are shown. E, IGF-I and AICAR increased endothelial cell numbers when given separately; however, when given together, no increases were found. *p < 0.001 and **p < 0.05 vs control (n = 4). F, Convergent stimulation of AMPK with AICAR and the IGF-IR with IGF-I results in significantly greater increases in glucose uptake in endothelial cells. Cultures received the respective treatments, and glucose use was monitored 24 h later. *p < 0.001 versus control; **p < 0.001 versus all other groups (n = 4).